Value Engineering Definition Meaning and How It Works
Contents
- 1 Value Engineering: Definition, Meaning, and How It Works
- 1.1 What Is Value Engineering?
- 1.2 Understanding Value Engineering
- 1.3 Ratio of Function to Cost
- 1.4 Steps in Value Engineering
- 1.5 Types of Value
- 1.6 Value Engineering vs. Value Analysis
- 1.7 What Is the Role of Value Engineering?
- 1.8 What Are the Phases of Value Engineering?
- 1.9 Why Is Value Engineering Important?
- 1.10 What Are the Types of Value in Value Engineering?
- 1.11 The Bottom Line
Value Engineering: Definition, Meaning, and How It Works
What Is Value Engineering?
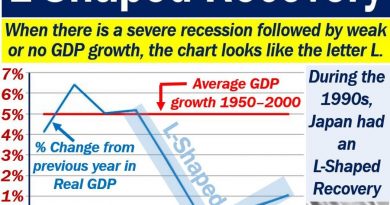
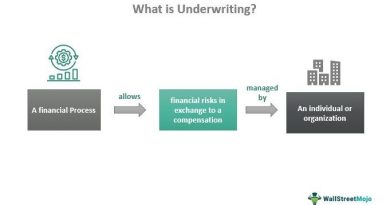
Value engineering is a systematic approach to providing necessary functions in a project at the lowest cost. It promotes the substitution of materials and methods with less expensive alternatives without sacrificing functionality. Value engineering focuses on the functions rather than the physical attributes of components and materials. It is also known as value analysis.
Key Takeaways
- Value engineering provides necessary functions in a project at the lowest cost.
- It promotes the substitution of materials and methods with less expensive alternatives without sacrificing functionality.
- Value engineering is often broken into six steps or phases from generating ideas to change implementation.
- It is primarily focused on the use, cost, esteem, and exchange values.
- Value is defined as function divided by cost, with the aim of maximizing function while minimizing cost.
Understanding Value Engineering
Value engineering is the review of new or existing products during the design phase to reduce costs and increase functionality. It aims to find the most cost-effective way to produce an item while maintaining its purpose. Cost reduction should not compromise the quality of the product.
Value engineering emerged during World War II when substitutes for materials and components were sought due to shortages. These substitutes were found to reduce costs without sacrificing performance.
Ratio of Function to Cost
Product value is defined as the ratio of function to cost. The function refers to the specific work an item is designed to perform, while the cost refers to the item’s life cycle cost. The value of a product can be increased by improving its function or decreasing its cost. Production, design, maintenance, and replacement costs are included in value engineering analysis.
Product Value = Function Cost
For example, a tech product with a two-year life cycle will be designed with cost-effective materials and resources that serve until the end of its life cycle, reducing costs.
Another company may maximize the function of a product with minimal cost by evaluating alternate ways to accomplish its function.
Steps in Value Engineering
Value engineering involves six steps, starting from information gathering and ending with change implementation.
Step 1: Gather Information
Analyze the product life cycle, including manufacturing, selling, and distribution-related expenses. Break down data sets and prioritize processes or elements for analysis.
Step 2: Think Creatively
Consider new approaches, take risks, and apply existing processes creatively. Generate ideas to reimagine the product’s development and distribution.
Step 3: Evaluate Ideas
Assess the pros and cons of each idea, considering their overall impact. Prioritize ideas with greater benefits and address potential disadvantages.
Step 4: Develop and Analyze
Analyze the best ideas in detail, considering financial projections, revised plans, and overall viability. Consider the impact on other departments and the organization’s financial capability.
Step 5: Present Discoveries
Present the best ideas to management, comparing alternatives and highlighting benefits. Include revised timelines, financial projections, and risk assessments.
Step 6: Implement Changes
Move forward with approved changes, forming new teams for implementation and monitoring progress.
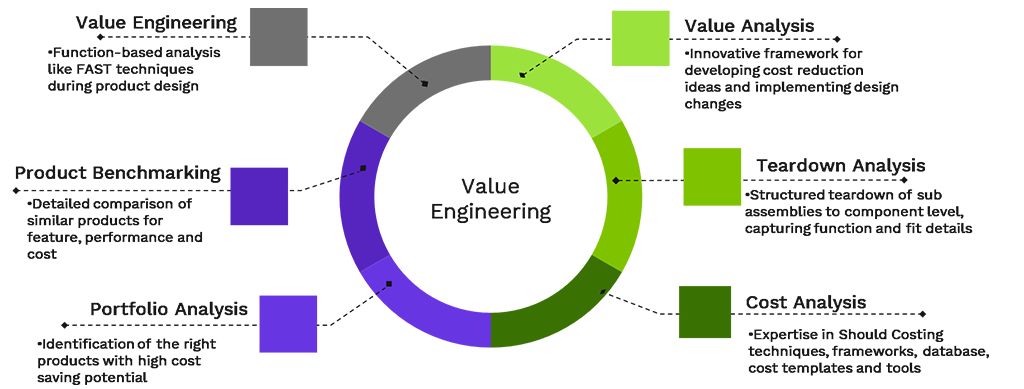
Types of Value
Value engineering considers four primary types of value: use value, cost value, esteem value, and exchange value.
Use Value
The value derived from the product’s attributes and purpose.
Cost Value
The cost required to produce the product.
Esteem Value
The intrinsic value associated with the brand or product beyond its physical benefits.
Exchange Value
The ease of buying or trading the product.
Value Engineering vs. Value Analysis
Value engineering occurs before product fabrication, while value analysis is used to analyze existing products. Value engineering focuses on preventing unnecessary costs or deficient value, while value analysis eliminates costs or negative value components. Value engineering is more manufacturing-oriented, while value analysis may be used in business or sales.
What Is the Role of Value Engineering?
Value engineering maximizes the value a customer receives from a product by balancing its functions and financial considerations. It aims to provide the greatest benefit to the consumer while minimizing costs.
What Are the Phases of Value Engineering?
Value engineering involves six stages: information gathering, brainstorming, evaluation, plan development, presentation, and implementation.
Why Is Value Engineering Important?
Value engineering ensures customer satisfaction and maximizes a product’s utility. By considering a product’s use, cost, and functionality, value engineering enhances profitability and guides future plans.
What Are the Types of Value in Value Engineering?
Value engineering recognizes use, cost, exchange, and esteem value. Other categories may be used to define consumer benefits, but the goal is to analyze all perceived or received values.
The Bottom Line
Value engineering prevents the waste of a product’s potential. By evaluating how a product can better serve customers and minimize costs, value engineering maximizes value and profitability.