Material Nonpublic Information MNPI Definition and Laws
Contents
- 1 Definition and Laws of Material Nonpublic Information (MNPI)
- 1.1 What Is Material Nonpublic Information?
- 1.2 Understanding Material Nonpublic Information
- 1.3 Material Nonpublic Information vs. Insider Trading
- 1.4 Types of Material Nonpublic Information
- 1.5 What Is Nonpublic Personal Information?
- 1.6 Is Insider Trading Illegal?
- 1.7 When Can Material Nonpublic Information Be Disclosed?
Definition and Laws of Material Nonpublic Information (MNPI)
Cierra Murry, a seasoned professional specializing in banking, credit cards, investing, loans, mortgages, and real estate, brings over 15 years of experience in financial analysis, underwriting, loan documentation, loan review, banking compliance, and credit risk management.
What Is Material Nonpublic Information?
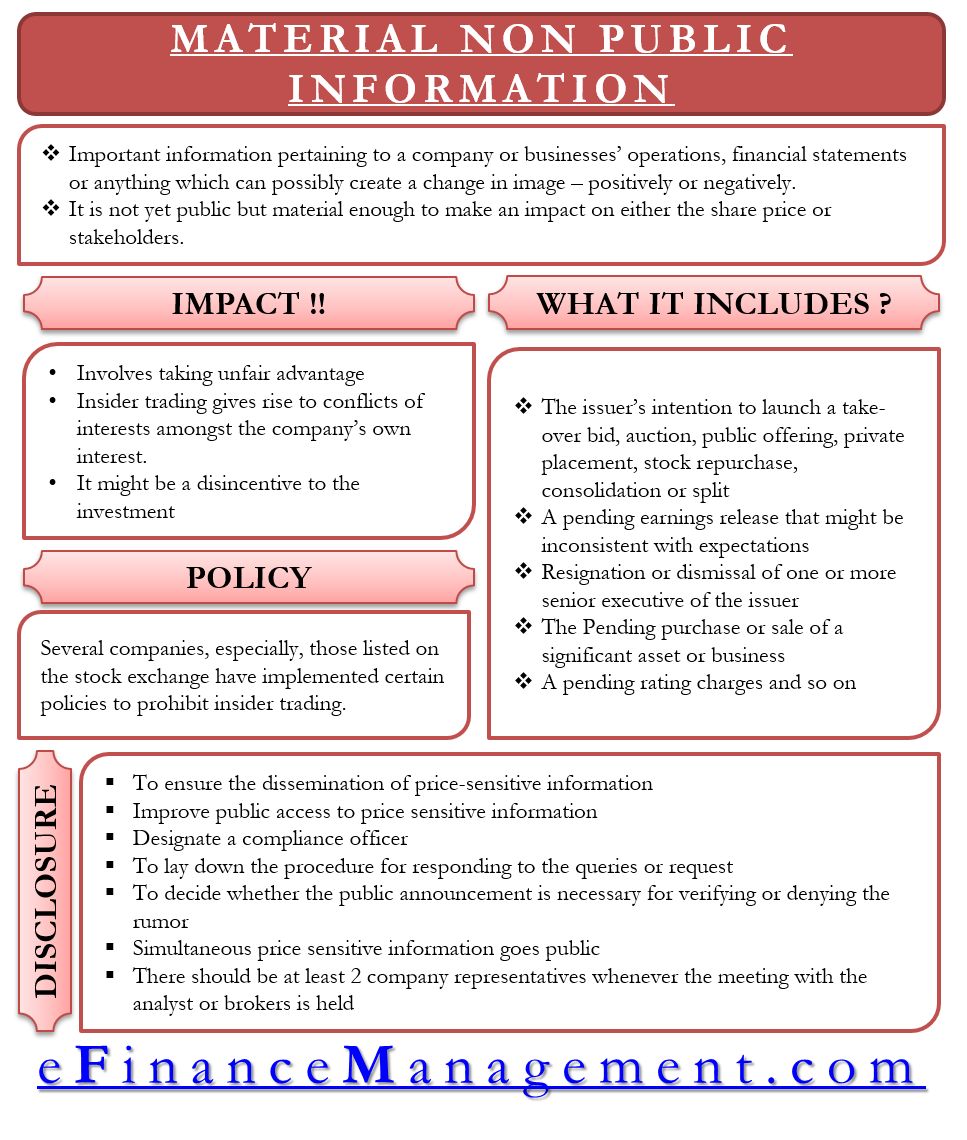
Material nonpublic information refers to data about a company that has not been made public but could affect its share price. It is illegal for individuals who possess nonpublic material information to use it to gain an advantage in stock trading and share this information for others to profit in the market.
Key Takeaways
- Material nonpublic information is undisclosed corporate news or information that may impact a company’s share price.
- Utilizing this information for personal trading gains or sharing it with others for market advantage is illegal.
- The manner in which one obtains nonpublic material information and their affiliation with the company is irrelevant from a legal standpoint.
- Insider trading involving nonpublic material information is against the law.
Understanding Material Nonpublic Information
It doesn’t matter how a person receives the material nonpublic information or their employment status with the company. For example, if someone learns nonpublic material information from a family member and shares it with a friend, and the friend uses it to profit in the stock market, all three individuals could face prosecution.
The best way to avoid legal trouble is to refrain from sharing material nonpublic information.
Learning in advance, before public disclosure, that a company’s expected earnings per share (EPS) for a specific quarter could be significantly lower than anticipated would be considered material nonpublic information. Obtaining information about ongoing lawsuits involving a company is another example.
Materiality is a crucial element in defining material nonpublic information. The information must be significant enough to influence a company’s stock price. If a checkout clerk at a large company learns that their working hours will be reduced the following month, although this is nonpublic information, it is not material because it won’t affect the stock price.
Material Nonpublic Information vs. Insider Trading
Contrary to common misconceptions, not all insider trading is illegal. Insiders are allowed to trade their company’s stock, provided their transactions are registered and filed with the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC).
Illegal insider trading occurs when material nonpublic information is used to gain an unfair advantage. For instance, if a marketing director at an automotive company overhears a conversation between the chief executive officer (CEO) and the chief financial officer (CFO), three days before the release of the company’s earnings, where the CFO reveals that the company missed its revenue forecasts and had losses in the previous quarter.
The person aware of the nonpublic information advises their cousin, who owns shares in the company, to sell them immediately. This is an example of material nonpublic information, as the most recent financial results have not been disclosed to the public yet.
If the cousin proceeds to sell the shares the next day, before the earnings numbers become public, it could be deemed illegal insider trading, as it grants an unfair advantage over other investors.
However, if the cousin waits to sell the shares until after the numbers are made public, the trade is more likely to be legal. At that point, the information would go from being nonpublic to publicly available.
Types of Material Nonpublic Information
Nonpublic material information can take various forms, sourced either internally from the affected company or externally from regulatory agencies, lawmakers, credit agencies, or financial institutions.
Other examples include essential financial filings like earnings reports. Upcoming corporate actions that may affect stock prices, such as initial public offerings (IPOs), acquisitions, stock buybacks, or splits, are also considered nonpublic material information.
The outcomes of pending legal proceedings, including lawsuit decisions and rulings by agencies like the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration, can likewise be classified as material nonpublic information.
What Is Nonpublic Personal Information?
Nonpublic information pertains to personal information about an individual that is not and should not be accessible to the public. This includes Social Security Numbers, banking information, other identifiable financial data, and specific financial institution transactions.
Is Insider Trading Illegal?
Insider trading becomes illegal when it involves the use of material nonpublic information. Having access to nonpublic information and making investment decisions based on it, especially if those decisions can impact the financial well-being of an entity, is considered illegal. It is a civil and criminal offense punishable by imprisonment and fines.
When Can Material Nonpublic Information Be Disclosed?
Material nonpublic information can be disclosed at a company’s discretion in compliance with the law. When a company publicly discloses material information on a large scale, it becomes widely available and can be utilized by all individuals, establishing a fair playing field for investors.