Trailing Earnings Per Share EPS What it is Examples
Trailing Earnings Per Share (EPS): What it is, Examples
What Is Trailing Earnings Per Share (EPS)?
Trailing earnings per share (EPS) is a company’s earnings generated over a prior period reported on a per-share basis.
The term "trailing" implies a value calculated on a rolling basis. Trailing EPS may describe the most recent 12-month period or four earnings releases. The period used for a trailing EPS will change as the most recent earnings are added to the calculation and earnings from five quarters ago are dropped.
Key Takeaways
– Trailing EPS refers to a company’s earnings per share over the previous four quarters.
– EPS is a measure of a company’s profitability.
– Trailing EPS shows what happened in the past, but does not forecast the future.
– To forecast future earnings, traders and analysts use models and earnings forecasts.
Understanding Trailing Earnings Per Share (EPS)
Earnings per share (EPS) is calculated as a company’s profit divided by the outstanding shares of its common stock. The resulting number serves as an indicator of a company’s profitability. A higher EPS indicates greater profitability.
The term "trailing" refers to "previous years," in contrast to a present or forward-looking EPS. Most recorded and quoted EPS values are trailing.
Trailing EPS often uses the previous four quarters of earnings in its calculation and has the benefit of using actual numbers instead of projections. Most price to earnings (P/E) ratios are calculated using the trailing EPS because it represents what has actually happened. However, investors also consider current and future EPS figures. Future EPS estimates are based on analyst expectations and are called earnings forecasts.
Trailing EPS for public companies are widely reported on financial news sites.
Growth or Decline in Trailing EPS
Growth investors analyze trailing EPS or yearly EPS to see if a company is increasing earnings quarter-over-quarter and year-over-year.
Investors want to see quarterly earnings increase relative to the same quarter in the prior year, as well as higher earnings for the fiscal year compared to the prior fiscal year. Trailing EPS can also be compared to the prior fiscal year. Ideally, trailing EPS will be higher.
Some growth investors also consider earnings forecasts and look for upward movement in future quarters.
A decline in the percentage increase from quarter to quarter or year-to-year suggests declining growth. This may be a warning sign for growth investors to start exiting long positions.
If quarterly or yearly EPS, or trailing EPS, is falling relative to prior figures, there is no growth and the company is experiencing a contraction. This is not what growth investors seek.
Example of Trailing EPS
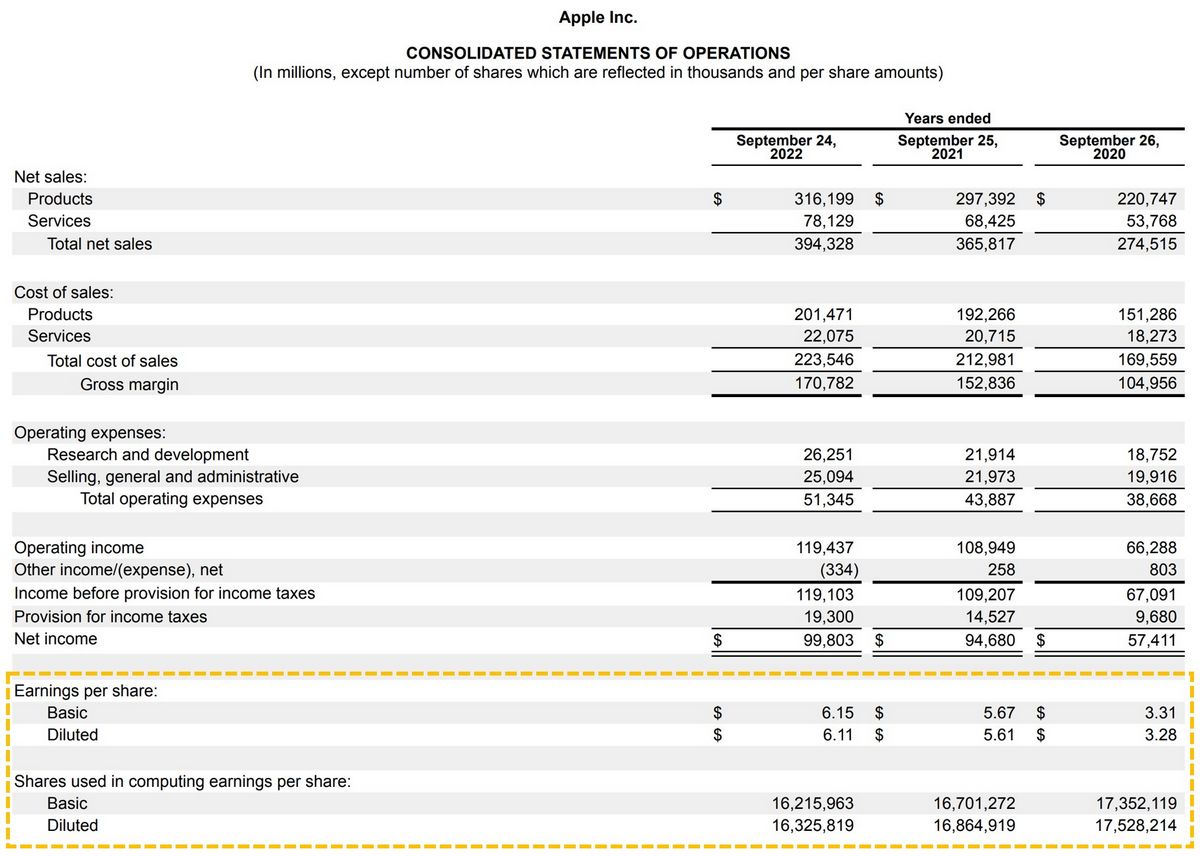
For example, let’s consider a hypothetical period for Apple Inc. (AAPL) earnings. Assume that on:
If these were the four most recent quarters, these figures would be used to generate the trailing EPS of $11.89.