Material Weakness What it is Its Impact and Examples
Material Weakness: What it is, Its Impact, and Examples
What Is Material Weakness?
A material weakness is when a company’s internal controls—activities, rules, and processes designed to prevent financial statement irregularities and improve operation efficiency—are ineffective. If a deficiency in internal control is a material weakness, it could result in a material misstatement in a company’s financial statements. This would make the company’s financial statement data unreliable and ineffective for assessing financial health and determining a reasonable stock price.
When an audit detects a material weakness in a company’s internal controls, the auditors report it to the audit committee. Every publicly-traded company in the US must have a qualified audit committee. The audit committee, part of the board of directors, requires the company’s management to rectify the material weakness.
Key Takeaways
– A material weakness exists when internal controls fail.
– When identified, a firm’s audit committee must remedy the weakness.
– An unresolved material weakness can result in a material misstatement – incorrect information in a financial statement that can alter the decisions of its users.
– US companies must follow Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) when preparing financial statements.
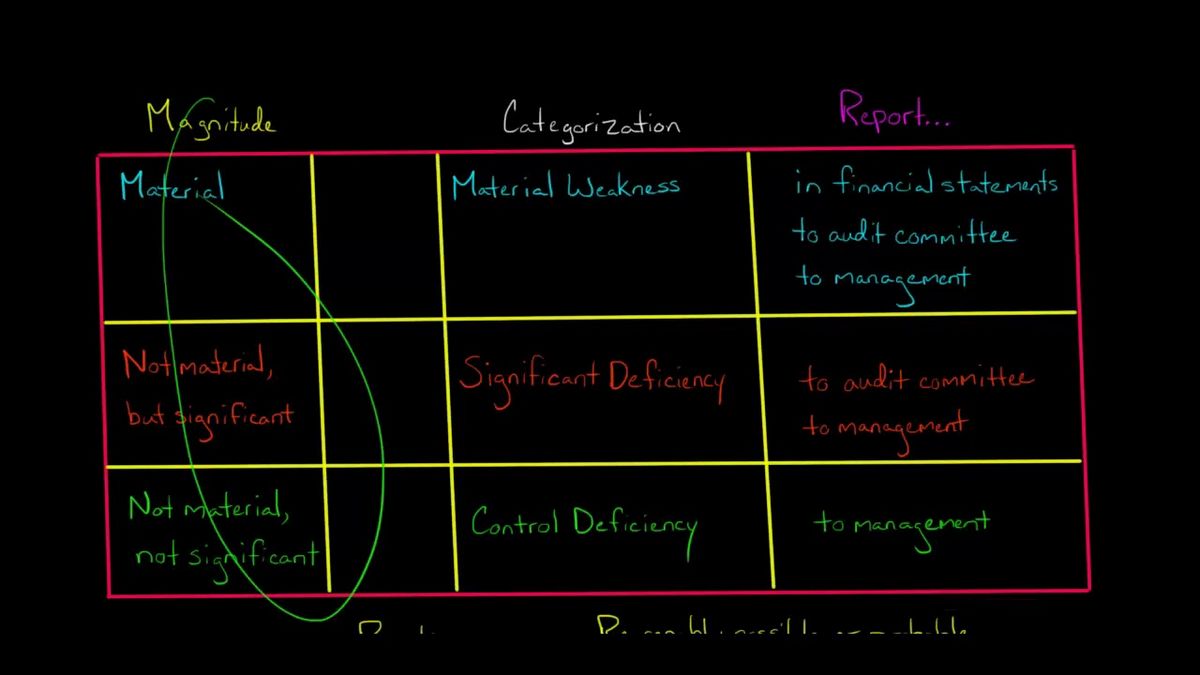
– A significant deficiency is less severe than a material weakness and refers to deficiencies in a company’s financial reporting.
Understanding Material Weakness
A material weakness, when reported by an auditor, suggests that a misstatement could occur. If a material weakness remains undetected and unresolved, a material misstatement could eventually occur in a company’s financial statements, affecting the company’s valuation.
In the US, companies must follow the Securities Exchange Committee (SEC) adopted Generally Accepted Accounting Principles (GAAP) when preparing financial statements. Most US firms subscribe to the 5% materiality rule, which states that misstated values 5% above bases (e.g., gross profit, net income, etc.) are material.
Material Weakness vs. Significant Deficiency
Material weakness and significant deficiency are sometimes used interchangeably, but they have different weights. A significant deficiency warrants attention but is less likely to impact financial statements as material weaknesses do. GAAP does not provide guidance on what are material weaknesses.
Example of a Material Weakness
For example, a $100 million overstatement in revenue would be a material misstatement for a company generating $500 million in sales annually. Incorrect company valuations, as a result of material weaknesses, may affect the company’s stock price. Prompt identification of material weaknesses in a company’s internal controls is crucial to maintain public trust.
In October 2018, Costco Wholesale (COST) reported a material weakness in its internal control related to general information technology controls. Unauthorized access to the company’s financial reporting systems was possible. Remediation efforts began immediately, and Costco completed their remediation efforts in 2019, concluding that its internal controls over financial reporting were tested and operating effectively.
What is the impact of a material weakness?
Material weaknesses can adversely affect a company’s reputation and value. A company’s stock price may drop as investors perceive it as risky. Depending on the severity of the weakness, the company may incur legal and additional external auditing fees. Employees, particularly management, may face disciplinary actions for oversight failures.
What is worse: significant deficiency or material weakness?
A material weakness is more severe than a significant deficiency. A material weakness creates a material misstatement in a company’s financial statements, while a significant deficiency negatively affects the company’s ability to record, process, summarize, and report financial information.
What are indicators of material weaknesses?
Some indicators of material weaknesses include fraud committed by senior leaders, financial misstatements missed by internal controls but caught by an auditor, and poor management of a company’s external and internal financial reporting.