What a Currency Forward Is How It Works Example Use in Hedging
Contents
- 1 What a Currency Forward Is, How It Works, Example, Use in Hedging
What a Currency Forward Is, How It Works, Example, Use in Hedging
What Is a Currency Forward?
A currency forward is a binding contract in the foreign exchange market that locks in the exchange rate for the purchase or sale of a currency on a future date. It is a customizable hedging tool that does not involve an upfront margin payment.
The major benefit of a currency forward is that its terms are not standardized and can be tailored to a particular amount and for any maturity or delivery period, unlike exchange-traded currency futures.
Key Takeaways
- Currency forwards are OTC contracts traded in forex markets that lock in an exchange rate for a currency pair.
- They are generally used for hedging and can have customized terms, such as a particular notional amount or delivery period.
- Unlike listed currency futures and options contracts, currency forwards do not require upfront payments when used by large corporations and banks.
- Determining a currency forward rate depends on interest rate differentials for the currency pair in question.
Understanding Currency Forwards
Unlike other hedging mechanisms such as currency futures and options contracts, currency forwards typically do not require an upfront payment when used by large corporations and banks.
However, a currency forward represents a binding obligation and requires a deposit from retail investors or smaller firms with whom financial institutions do not have a business relationship to compensate for the risk of non-delivery or non-settlement.
Currency forward settlement can be on a cash or a delivery basis, provided that the option is mutually acceptable and has been specified beforehand in the contract. Currency forwards are over-the-counter (OTC) instruments, also known as “outright forwards.”
Importers and exporters generally use currency forwards to hedge against fluctuations in exchange rates.
Example of a Currency Forward
The mechanism for computing a currency forward rate depends on interest rate differentials for the currency pair.
For example, assume a current spot rate for the Canadian dollar of US$1 = C$1.0500, a one-year interest rate for Canadian dollars of 3 percent, and the one-year interest rate for US dollars of 1.5 percent.
After one year, based on interest rate parity, US$1 plus interest at 1.5 percent would be equivalent to C$1.0500 plus interest at 3 percent:
- $1 (1 + 0.015) = C$1.0500 x (1 + 0.03)
- US$1.015 = C$1.0815, or US$1 = C$1.0655
The one-year forward rate in this instance is US$ = C$1.0655. Note that because the Canadian dollar has a higher interest rate than the US dollar, it trades at a forward discount to the greenback. The actual spot rate of the Canadian dollar one year from now has no correlation with the one-year forward rate at present.
The currency forward rate is based on interest rate differentials and does not incorporate investors’ expectations of where the actual exchange rate may be in the future.
Currency Forwards and Hedging
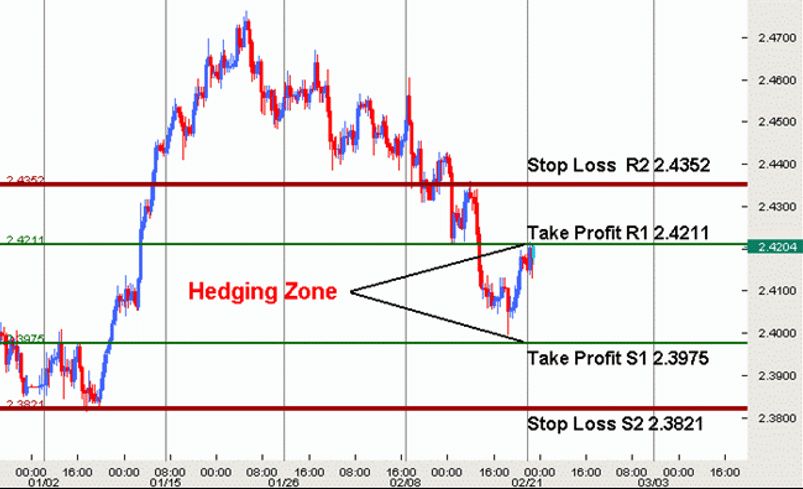
How does a currency forward work as a hedging mechanism? Assume a Canadian export company is selling US$1 million worth of goods to a U.S. company and expects to receive the export proceeds a year from now. The exporter enters into a forward contract to sell $1 million a year from now at the forward rate of US$1 = C$1.0655.
If a year from now, the spot rate is US$1 = C$1.0300 (as anticipated by the exporter), by locking in the forward rate, the exporter benefits by C$35,500. On the other hand, if the spot rate a year from now is C$1.0800 (contrary to the exporter’s expectations), the exporter incurs a notional loss of C$14,500.
What Is the Difference Between Currency Forwards and Currency Futures?
Currency forwards and futures are similar. The main difference is that currency futures have standardized terms and are traded on exchanges such as the Chicago Mercantile Exchange (CME), whereas forwards have customizable terms and are traded over-the-counter (OTC).
Why Are Currency Forwards Used?
Currency forwards are used to lock in an exchange rate for a certain period of time. This is often used to hedge foreign currency exposure.
Which Currencies Can Currency Forwards Be Written on?
Because they are customizable and trade OTC, currency forwards can appear on any number of currency pairs. The specific pairs would be determined by the counterparties involved in the trade.
Because they are customizable and trade OTC, currency forwards can appear on any number of currency pairs. The specific pairs would be determined by the counterparties involved in the trade.