United Nations Global Compact Definition Purpose 10 Principles
Contents
- 1 United Nations Global Compact: Definition, Purpose, 10 Principles
United Nations Global Compact: Definition, Purpose, 10 Principles
What Is the United Nations Global Compact?
The United Nations Global Compact is a strategic initiative that supports global companies committed to responsible business practices in human rights, labor, the environment, and corruption. This UN-led initiative promotes activities that contribute to sustainable development goals.
Key Takeaways
- The United Nations Global Compact is an initiative that global corporations can sign on to, committing to responsible business practices.
- The UN Global Compact has 10 operating principles outlining these values.
- For example, a corporation within the UN Global Compact could commit to providing free Wi-Fi access in remote areas.
Understanding the United Nations Global Compact
The UN Global Compact is based on 10 principles that define a company’s value system and approach to business. These principles were founded in the Universal Declaration of Human Rights, the International Labor Organization’s Declaration on Fundamental Principles and Rights at Work, the Rio Declaration on Environment and Development, and the UN Convention Against Corruption. Member companies engage in specific business practices that benefit people and the planet while pursuing profitability with integrity.
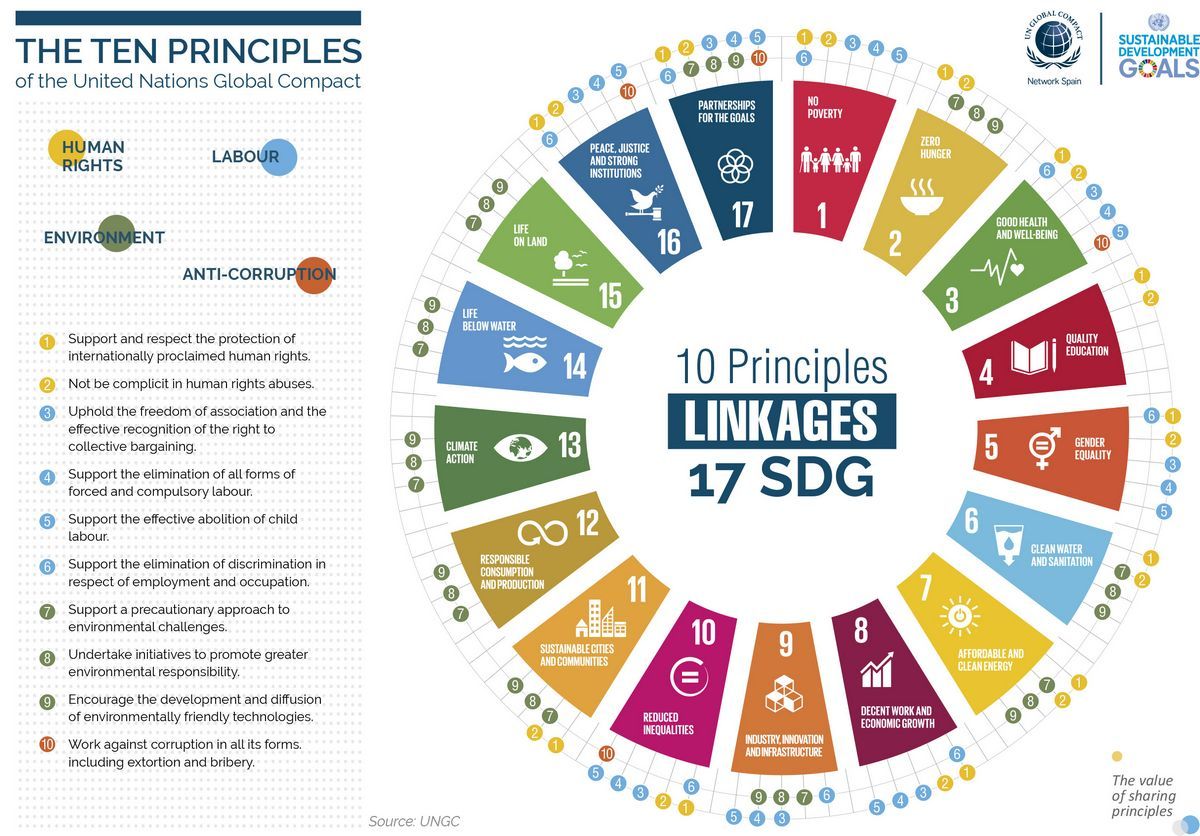
The United Nations Global Compact’s 10 Principles for Businesses
The 10 principles for businesses, as stated on the UN Global Compact’s website, are:
- Principle 1: Support and respect internationally proclaimed human rights.
- Principle 2: Ensure business practices are not complicit in human rights abuses.
- Principle 3: Uphold freedom of association and the effective recognition of the right to collective bargaining.
- Principle 4: Eliminate all forms of forced and compulsory labor.
- Principle 5: Abolish child labor.
- Principle 6: Eliminate discrimination in employment and occupation.
- Principle 7: Adopt a precautionary approach to environmental challenges.
- Principle 8: Conduct environmentally responsible activities.
- Principle 9: Encourage the development and diffusion of environmentally friendly technologies.
- Principle 10: Fight corruption in all its forms, including extortion and bribery.
Companies that join the compact integrate these principles into their corporate strategies, culture, and day-to-day operations. They are expected to advocate the principles publicly and communicate with stakeholders on progress.
Member Company Responsibilities of the UN Global Compact
Member companies are expected to act in environmentally responsible ways and recognize the link between environmental issues and social and development priorities.
Member companies must also focus on social sustainability and human rights as they apply to labor, women’s empowerment, gender equality, children, indigenous peoples, people with disabilities, and people living in poverty. The compact believes that protecting human rights is primarily a government responsibility but businesses should contribute or, at a minimum, avoid harm.
Ways in which businesses can contribute to human rights include creating jobs, developing goods and services that help people meet basic needs, promoting public policies that support social sustainability, partnering with other businesses to have a greater impact, and making strategic social investments.
Incentives for Businesses to Support the UN Global Compact
Companies might join the compact because of the importance of corporate codes of conduct for developing and maintaining positive relationships and to avoid regulatory and legal problems. Businesses may support the compact for the greater good, but also because operating in environments associated with poverty and inequality where the rule of law is weak can harm the company’s reputation and bottom line.
Further, companies that commit to sustainability may have an advantage in accessing untapped markets, attracting and retaining business partners, developing innovative products and services, and encouraging employee satisfaction and productivity.
An example of sustainable activity by a member company is supporting inclusive, equitable, quality education and promoting lifelong learning opportunities for all. A company might partner with governments and other companies to create open-source technology, delivering education to hard-to-reach communities and developing low-cost learning materials for under-resourced schools.