Merchant Category Codes MCC Definition Purposes and Examples
Contents
- 1 Merchant Category Codes (MCC): Definition, Purposes, and Examples
- 1.1 What Are Merchant Category Codes (MCCs)?
- 1.2 Understanding Merchant Category Codes
- 1.3 Examples of Merchant Category Codes
- 1.4 How Consumers Can Use MCCs to Maximize Their Rewards
- 1.5 How Can You Find the Merchant Category Code for a Business?
- 1.6 What Is an Interchange Fee?
- 1.7 What Is a 1099 Tax Form?
- 1.8 The Bottom Line
Merchant Category Codes (MCC): Definition, Purposes, and Examples
What Are Merchant Category Codes (MCCs)?
Merchant category codes (MCCs) are four-digit numbers that credit card issuers use to classify purchases according to the type of merchant. MCCs serve various purposes, including calculating and issuing credit card rewards.
Key Takeaways
- MCCs are four-digit numbers assigned to different types of businesses.
- MCCs are used in credit and debit card transactions for tax reporting and calculating cash back rewards.
- MCCs can affect the fees that merchants pay for accepting card payments.
Understanding Merchant Category Codes
Every credit card transaction is assigned an MCC based on the involved business.
MCCs have various uses. They help calculate consumer rewards, determine tax reporting requirements, and impact merchant fees for accepting payment cards.
MCCs are based on International Organization for Standardization (ISO) and Standard Industrial Classification (SIC) codes but may be adapted by card networks. For example, Visa consolidates SIC codes into MCCs and establishes non-corresponding MCCs for certain merchants.
While many MCCs are recognized across card issuers and networks, others may vary. Some merchants have multiple MCCs, and the codes may change over time.
Here are examples of how MCCs are used.
- If a consumer has a credit card offering 3% cash back on airline travel, they should receive that reward on any purchase classified under MCC 4511 for airlines and air carriers.
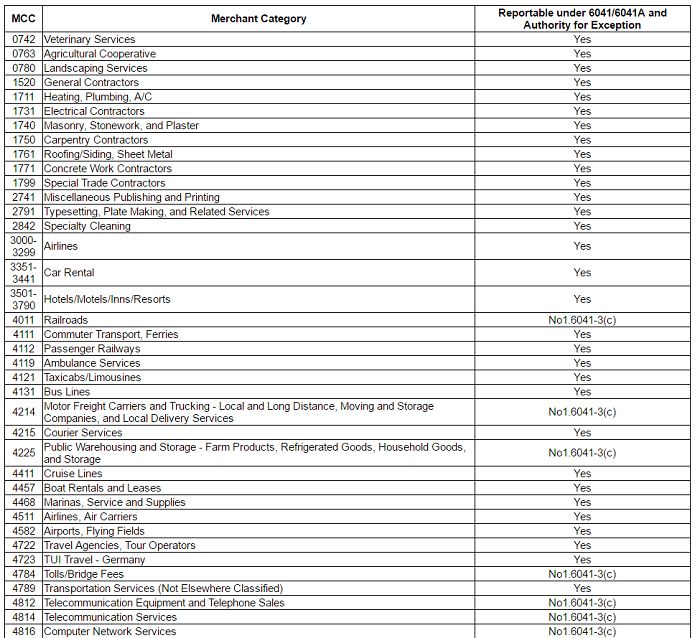
- Companies must report purchases of services from individuals or non-employees to the IRS. MCCs can help determine if the transaction is reportable. Product purchases do not require reporting.
- The MCC assigned to a business can dictate the interchange fee it pays to its card processor. For instance, a business classified under the MCC for gas stations but rents cars may have different fees than a car rental company.
Note
Some merchants, such as airlines and hotel chains, may have unique MCCs.
Examples of Merchant Category Codes
These are some MCCs related to travel and transportation used by Citibank.
| 4011 | Railroads – Freight |
| 4111 | Suburban and Local Commuter Passenger Transportation, Including Ferries |
| 4112 | Passenger Railways |
| 4119 | Ambulance Services |
| 4121 | Taxicabs and Limousines |
| 4131 | Bus Lines |
| 4214 | Motor Freight Carriers, Trucking, Moving & Storage, Local Delivery |
| 4215 | Courier Services and Freight Forwarders |
| 4225 | Warehousing or Storage of Farm Products, Refrigerated & Household Goods |
| 4411 | Cruise Lines |
| 4457 | Boat Leases and Rentals |
| 4468 | Marinas & Marine Service/Supplies |
| 4511 | Airlines and Air Carriers |
| 4582 | Airports and Airport Terminals |
| 4722 | Travel Agencies and Tour Operators |
| 4784 | Bridge and Road Fees and Tolls |
Source: Citibank
How Consumers Can Use MCCs to Maximize Their Rewards
Consumers with rewards cards can earn more rewards by knowing their MCCs.
For example, if you have a credit card offering 3 points for every $1 spent at restaurants, the MCC determines whether a transaction took place at a restaurant. If an establishment is classified as a grocery store, you won’t earn 3 points per $1. In this case, using a different card that gives 3% back on groceries would maximize cash back.
The same applies to grocery shopping at big-box stores like Walmart, as the assigned MCC may affect rewards eligibility.
If a credit card issuer fails to provide the correct amount of points or cash back based on the MCC, you can use this information to have the error rectified.
How Can You Find the Merchant Category Code for a Business?
Your monthly credit card statement may show how your transactions were classified. Alternatively, the card issuer or merchant can provide the specific MCC. Merchants can contact their card processor to confirm their MCC. Some card networks and issuers also publish MCC lists online.
What Is an Interchange Fee?
Merchants must pay an interchange fee to card networks and issuers for each credit or debit card transaction, commonly known as a swipe fee.
What Is a 1099 Tax Form?
A 1099 form reports types of income other than wages. Different 1099 forms exist, including 1099-INT for interest income and 1099-DIV for dividend income. When paying non-employees for services, businesses use a 1099-NEC to report payments exceeding $600. The recipient and the IRS receive this information.
The Bottom Line
Credit and debit card transactions are assigned MCC numbers based on merchant types. Understanding MCCs is beneficial for cardholders with rewards programs, especially those with varying rewards levels for different types of purchases.