Value Stock What It Is Examples Pros and Cons
Value Stock: What It Is, Examples, Pros and Cons
Tim Smith has over 20 years of experience in the financial services industry as both a writer and a trader.
What Is a Value Stock?
A value stock is shares of a company that appears to trade at a lower price relative to its fundamentals, such as dividends, earnings, or sales, making it appealing to value investors.
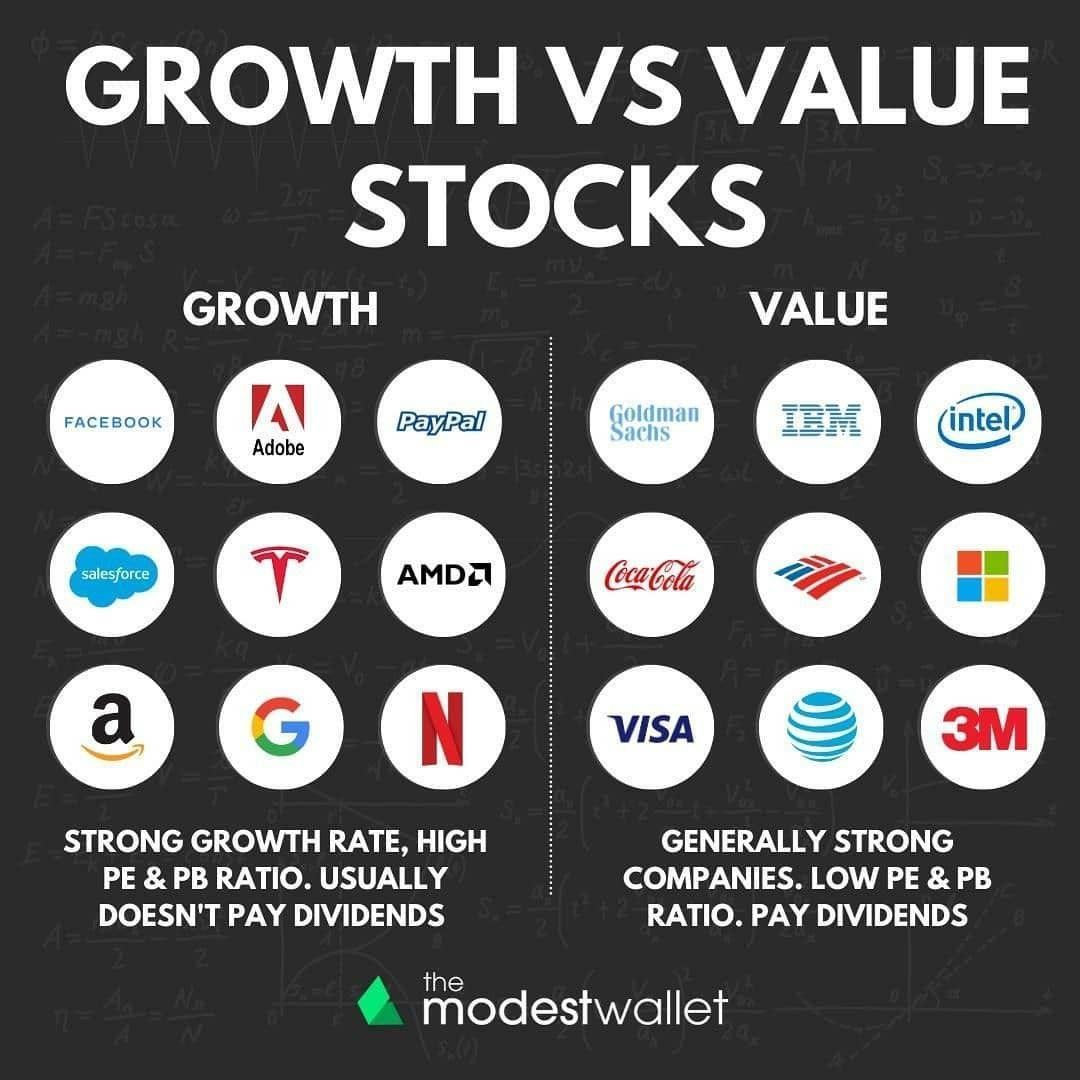
A value stock can be contrasted with a growth stock.
Key Takeaways:
– A value stock is trading below its fundamentals.
– Characteristics of value stocks include high dividend yield, low P/B ratio, and low P/E ratio.
– A value stock has a bargain price and is different from a growth stock.
– Value stocks issue dividends while growth stocks rely on cash for development.
Understanding Value Stocks:
A value stock is a security trading at a lower price than what the company’s performance may indicate. Investors in value stocks attempt to capitalize on market inefficiencies.
Common characteristics of value stocks include high dividend yield, low P/B ratio, and low P/E ratio. Investors can find value stocks using the "Dogs of the Dow" strategy.
In contrast to value stocks, growth stocks are equities of companies with strong growth potential. A balanced portfolio holds both value and growth stocks.
How to Determine and Invest in Value Stocks:
A value stock has a bargain price as investors see the company as unfavorable. It may come from a mature company experiencing adverse events. Companies that have recently issued equities have high-value potential.
Investors can invest in value stocks directly or through ETFs and mutual funds.
Several ways to analyze a stock’s value include evaluating the PE ratio, PB ratio, dividend yield, company growth, and industry comparison.
Why Are Some Stocks Undervalued?
Stocks may be undervalued due to investor mood, unfavorable news, poor financial performance, or macroeconomic concerns. Stocks of smaller companies may be undervalued due to lack of investor knowledge.
A single company can transition from a growth stock to a value stock.
Value Stocks vs. Growth Stocks:
Value stocks focus on finding stocks cheap in comparison to intrinsic value, while growth stocks seek stocks with growth potential.
Traditional valuation indicators are used for value stocks, while unconventional metrics are used for growth stocks.
Value stocks are associated with well-established businesses, while growth stocks are found in sectors with growth potential.
Value stocks emphasize dividends, while growth stocks reinvest profits for growth.
Value stocks are less risky than growth stocks.
Example of Value Stock:
Honda Motor (HMC) produces and sells various products worldwide. The company may be undervalued due to specific factors. Honda has a reputation for quality and is implementing a cost-cutting plan. It also aims to have 100% of their vehicles be electric in North America by 2040.
Are Value Stocks a Good Investment?
Value stocks may be a good investment for lower-risk investors who prefer established companies.
How Do You Profit From a Value Stock?
You can profit by buying and holding a value stock. Value stocks may take longer to appreciate, but they often issue dividends.
Are Value Stocks High Risk?
Value stocks are generally less risky than growth stocks, but both are equities and carry inherent risk.
Are Value Stocks Better Than Growth Stocks?
It depends on individual investment goals, risk tolerance, and market conditions. Both value and growth stocks have their advantages and performance may vary.
The Bottom Line:
A value stock is a class of stock that appears cheap relative to its intrinsic worth. Value stocks are associated with financially strong businesses with well-established market positions.



