Ring-Fence Definition in Finance Accounting and Legality
Contents
- 1 Ring-Fence: Definition in Finance Accounting and Legality
- 1.1 What Does Ring-Fence Mean?
- 1.2 Understanding Ring-Fences
- 1.3 Advantages and Disadvantages of Ring-Fencing
- 1.4 Offshore Ring-Fencing
- 1.5 What Is the Objective of Ring-Fencing?
- 1.6 Why Was Ring-Fencing Introduced in the United Kingdom?
- 1.7 What Is the British Government’s Threshold for Ring-Fencing?
- 1.8 The Bottom Line
Ring-Fence: Definition in Finance Accounting and Legality
What Does Ring-Fence Mean?
The term ring-fence refers to the creation of a virtual barrier that segregates a portion of a company’s financial assets. This may be done to reserve money for a specific purpose, reduce taxes, or protect assets from losses. Moving assets offshore to lower taxes is one example of ring-fencing.
Key Takeaways
- A ring-fence segregates some of a company’s assets.
- Offshore banking is sometimes referred to as ring-fencing assets.
- Ring-fencing can protect assets.
Understanding Ring-Fences
The term has its origins in the ring-fences that keep farm animals in and predators out. In financial accounting, it is used to describe strategies that protect assets.
Ring-fencing may involve transferring assets from one high-tax jurisdiction to another with lower or no taxes. It may be used to reserve money for a specific purpose or make it unavailable for another purpose.
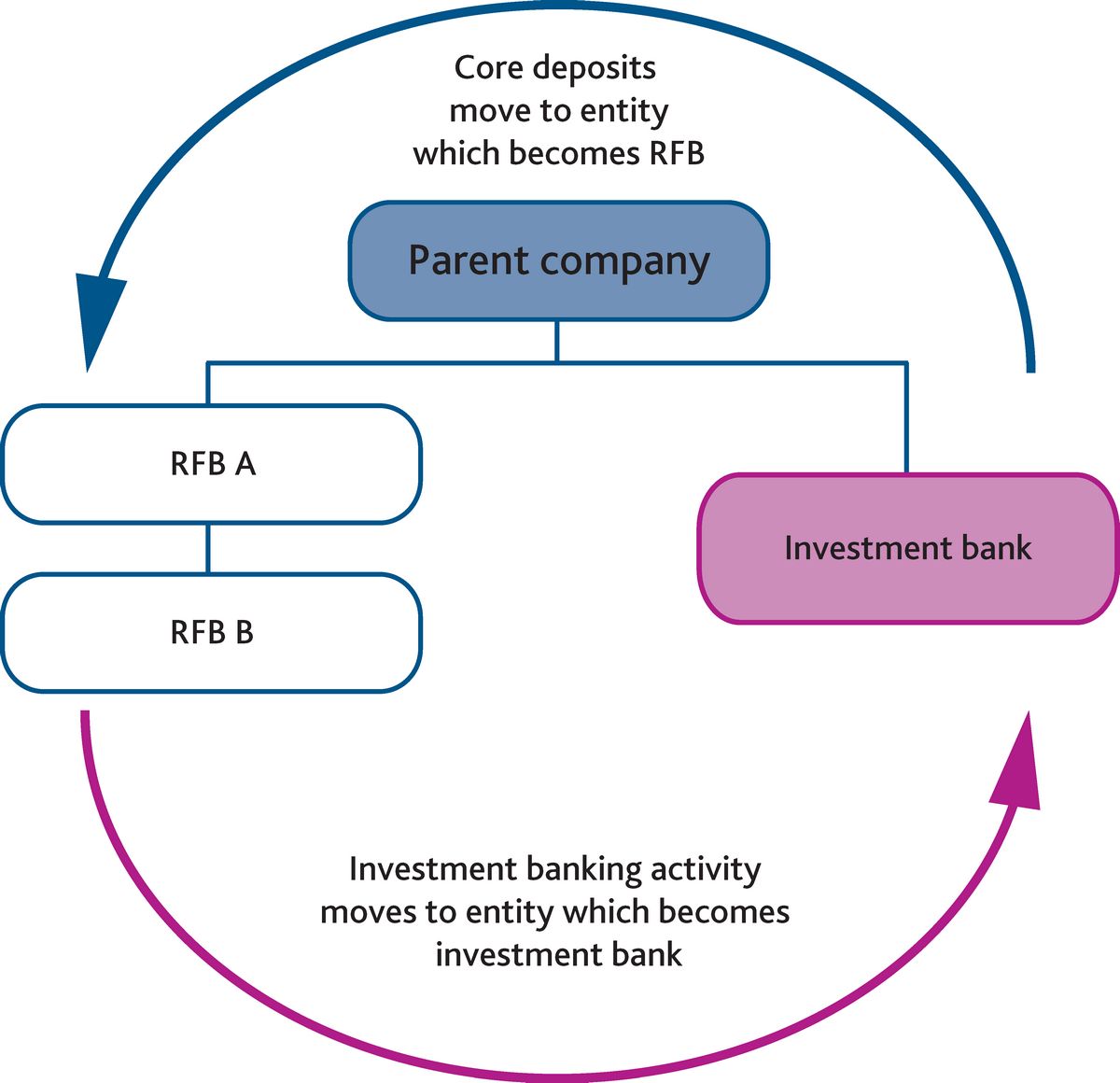
The British ring-fencing law, effective since 2019, requires financial institutions to ring-fence their consumer banking activities. This law aims to protect customer bank deposits from potential investment banking losses.
Britain passed a law in 2019 that requires financial institutions to ring-fence their everyday banking activities from their investment arms. Ring-fencing applies to banks with over £25 billion in core deposits.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Ring-Fencing
Advantages
One benefit of ring-fencing is that it provides protection for business assets from market risk, volatility, taxation, insolvency, and seizures.
This strategy helps keep the financial system sound and provides banks with a safety net. It puts less burden on taxpayers if banks succumb to economic pressure in the future.
Disadvantages
Separating groups of assets may lead to a reduction in oversight and weakening of risk management.
Banks and organizations required to ring-fence may take advantage of this requirement to obtain more favorable tax treatment by moving assets offshore, which could reduce tax revenue for the home country.
- Protects against certain risks
- Leads to a safer and secure financial system
- Reduces oversight and weakens risk management
- Moving certain assets offshore may lead to drop in tax revenue
Offshore Ring-Fencing
In the U.S., the term describes the transfer of assets from one jurisdiction to another, usually offshore, to reduce an investor’s income or tax bill. It may also shield assets from seizure by debtors.
Ring-fencing assets to reduce taxation or avoid regulation is legal as long as it stays within the limits set in the laws and regulations of the home country.
Ring-fencing can also describe earmarking assets for a particular purpose, such as protecting a savings account for retirement.
What Is the Objective of Ring-Fencing?
The primary goal of ring-fencing is to separate one group of assets from another to protect core assets from volatility and other risks. It is common with banks to separate their core retail banking from their investment arms if they are deemed "too big to fail."
Why Was Ring-Fencing Introduced in the United Kingdom?
Ring-fencing was introduced by the British government in January 2019 to strengthen the country’s banking and financial system. It requires banks to divide their core retail banking from other divisions to protect the retail banking sector from riskier ventures.
What Is the British Government’s Threshold for Ring-Fencing?
The British government introduced a £25 billion threshold on core deposits when it implemented the ring-fencing rule in January 2019. Eligible banks must ring-fence assets above this limit as of 2023. The government is reviewing proposals to further strengthen the country’s banking and financial sector.
The Bottom Line
Risky investment ventures and a lack of oversight led to major losses, failing banks, and bailouts during the financial crisis. Ring-fencing was introduced in countries like the United Kingdom to protect banks’ core retail function and shield taxpayers from bearing the financial burden of bailing out banks in an economic crisis.