Wealth Management Meaning and What Wealth Managers Charge
Wealth Management Meaning and What Wealth Managers Charge
What Is Wealth Management?
Wealth management is an investment advisory service that combines financial services to address the needs of affluent clients. Using a consultative process, the advisor gleans information about the client’s wants and tailors a personalized strategy that uses financial products and services.
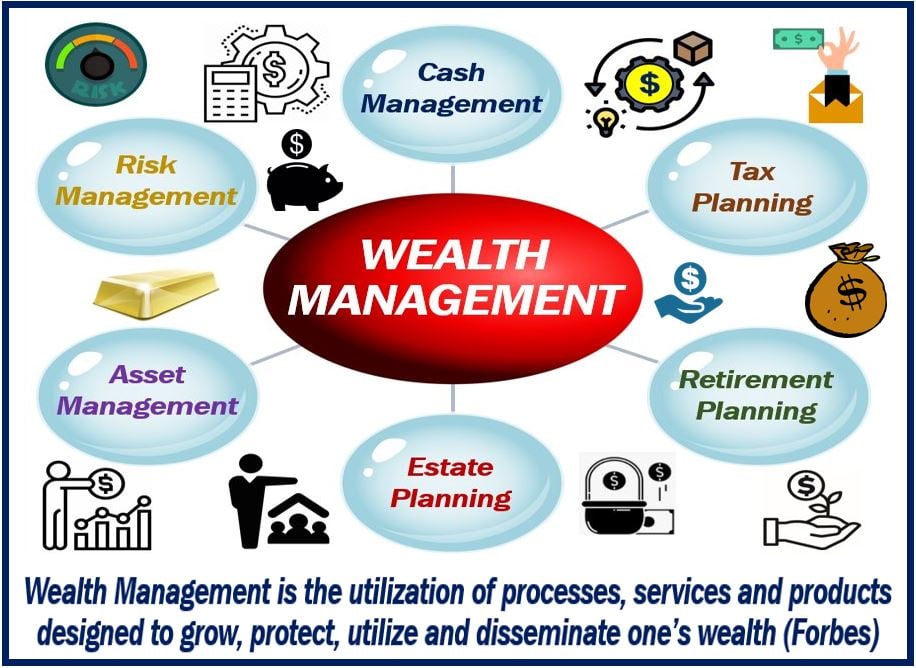
Typically, a holistic approach is taken within wealth management. To meet the needs of a client, a range of services may be provided, such as investment advice, estate planning, accounting, retirement, and tax services. Fees are based on a client’s assets under management (AUM).
Key Takeaways:
– Wealth management is an investment advisory service for affluent clients.
– A wealth management advisor manages an affluent client’s wealth holistically for one set fee.
– This service is usually appropriate for wealthy individuals with diverse needs.
Understanding Wealth Management
Wealth management is more than just investment advice. It encompasses all parts of a person’s financial life. Instead of integrating advice and products from multiple professionals, high net worth individuals may benefit from an integrated approach. A wealth manager coordinates the services needed to manage their clients’ assets and create a strategic plan for their current and future needs, such as will and trust services or business succession plans.
Many wealth managers can provide services in any aspect of the financial field, but some choose to specialize in areas such as cross-border wealth management. This may be based on the expertise of a specific wealth manager or the primary focus of the business.
In certain instances, a wealth management advisor may have to coordinate input from outside financial experts, as well as the client’s own service professionals, to craft the optimal strategy to benefit the client. Some wealth managers also provide banking services or advice on philanthropic activities.
Wealth Management Example
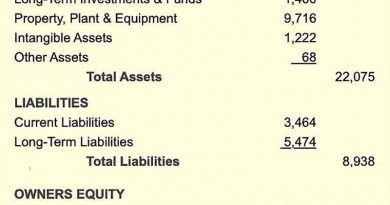
Wealth management offices have a team of experts and professionals available to provide advice across different fields. For instance, consider a client who has $2 million in investable assets, in addition to a trust for their grandchildren, and a partner who has recently passed away. A wealth management office would invest these funds in a discretionary account and provide will and trust services required for tax minimization and estate planning.
Wealth management advisors in the direct employ of an investment firm may have more knowledge in investment strategy, while those who work for a large bank may focus on the management of trusts, estate planning, or insurance options.
Wealth Management Business Structures
Wealth managers may work in a small-scale business or a larger firm associated with the finance industry. Depending on the business, wealth managers may function under different titles, including financial consultant or financial advisor. A client may receive services from a single designated wealth manager or have access to members of a specified wealth management team.
Fees for a Wealth Manager
Advisors can charge for their services in several ways. Some work as fee-only advisors and charge an annual, hourly, or flat fee. Some work on commission and are paid through the investments that they sell. Fee-based advisors earn a combination of a fee plus commissions on the investment products that they sell.
A recent survey of financial advisors finds the median advisory fee (up to $1 million AUM) is around 1%. However, some advisors charge more, especially on smaller account balances. Individuals with larger balances can often pay less, with the median AUM fee declining as assets increase.
Credentials for Wealth Managers
Check the credentials of a professional to see which designation and training might best suit your needs and situation. The top three professional advisor credentials are Certified Financial Planner, Chartered Financial Analyst, and Personal Financial Specialist. Websites for professional certifying organizations allow you to vet if a member is in good standing or has had disciplinary actions or complaints.
The Financial Industry Regulatory Authority (FINRA) has a tool that explains professional designations and whether the issuing organization requires continuing education, takes complaints, or has a way for you to confirm who holds the credentials.
Strategies of a Wealth Manager
The wealth manager develops a plan to maintain and increase a client’s wealth based on their financial situation, goals, and risk tolerance. Each part of a client’s financial picture, whether it is tax planning or wills and estates, is coordinated to protect the client’s wealth. This may coincide with financial projections and retirement planning.
After developing the plan, the manager meets regularly with clients to update goals, review, and rebalance the financial portfolio. They may investigate whether additional services are needed, with the ultimate goal of remaining in the client’s service throughout their lifetime.
What Do Wealth Managers Earn?
According to Indeed, the average salary for a wealth manager in the United States in 2022 was $79,395.
Is a Wealth Manager the Same as a Financial Planner?
While some financial professionals are both wealth managers and planners, a key difference is that wealth managers focus on assets and investments, while planners also consider everyday household finances and insurance needs.
How Much Money Does the Wealth Management Industry Manage?
As of 2020, the wealth management industry had AUM of upwards of $112 trillion globally. This figure is expected to grow to $145.4 trillion by 2025.