What Are Asset Classes More Than Just Stocks and Bonds
Asset Classes: More Than Just Stocks and Bonds
What Is an Asset Class?
An asset class is a grouping of investments with similar characteristics and subject to the same laws and regulations. Asset classes consist of instruments that behave similarly in the marketplace.
Examples of asset classes include equities, fixed income, commodities, and real estate.
Key Takeaways
– Asset classes are groups of investments with similar characteristics and governed by the same laws and regulations.
– Equities (stocks), fixed income (bonds), cash equivalents, real estate, commodities, and currencies are common examples of asset classes.
– Different asset classes usually have little correlation and sometimes even negative correlation.
– Financial advisors use asset classes to help investors diversify their portfolios.
Understanding Asset Classes
An asset class is a grouping of comparable financial securities. For example, IBM, MSFT, and AAPL are stocks grouped together. Asset classes and categories are often mixed. There is little correlation and sometimes negative correlation among different asset classes, making this important in investing.
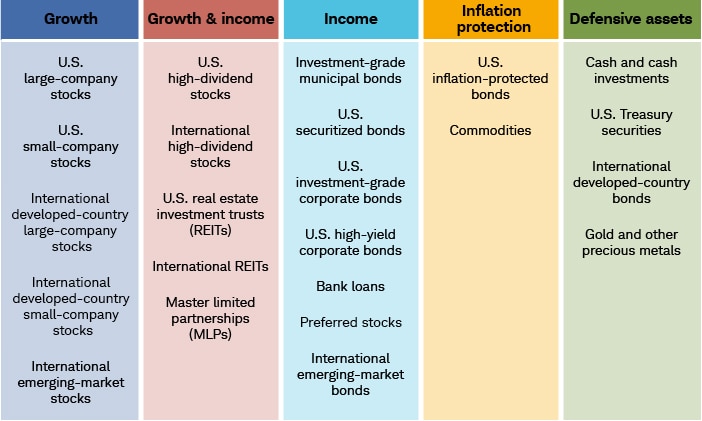
Historically, equities (stocks), fixed income (bonds), and cash equivalents were the main asset classes. However, real estate, commodities, futures, financial derivatives, and cryptocurrencies are now commonly included. Investment assets can be tangible or intangible instruments bought and sold to generate additional income, short- or long-term.
Financial advisors view investment vehicles as asset class categories for diversification. Each asset class has different risk and return characteristics. Investors diversify their portfolios by combining assets from different asset classes with different cash flow streams and levels of risk. Diversification reduces risk and increases the chance of positive returns.
The main asset classes are equities, fixed income, cash or marketable securities, and commodities.
Types of Asset Classes
The most common asset classes are:
Cash and Cash Equivalents:
This type of investment represents actual cash and highly liquid securities. It carries very low risk and lower returns compared to other asset classes.
Fixed Income:
Fixed income investments pay a fixed income. When you lend money to an entity, they pay you a fixed amount until the maturity date. Government and corporate bonds are common fixed-income products. Bonds pay interest based on inflation and perceived default risk.
Equities:
Equities refer to owning shares in a company. Profits can be made through dividends or selling shares at a higher price. Share prices can be volatile, and companies may go bankrupt.
Commodities:
Commodities are basic goods transformable into other goods and services. They include metals, energy resources, and agricultural goods. Commodities are considered a hedge against inflation and have returns based on supply and demand dynamics.
Alternative Asset Classes
Real estate and valuable inventory such as artwork and collectibles are alternative asset classes. Hedge funds, venture capital, crowdsourcing, and cryptocurrencies are also considered alternative investments. An asset’s illiquidity does not determine its return potential but may require more time to convert to cash.
Asset Class and Investing Strategy
Investment strategies seek alpha returns. Criteria tied to growth, value, income, or other factors help identify and categorize investment options. Some analysts focus on performance and valuation metrics, while others prioritize asset types or classes. Diversification among asset classes is advised to spread bets and reduce risk.
What are the most popular asset classes?
Historically, equities, fixed income, and cash equivalents were the main asset classes. Today, real estate, commodities, futures, financial derivatives, and cryptocurrencies are commonly included.
Which asset class has the best historical returns?
The stock market has historically produced the highest returns. The compound annual growth rate (CAGR) for the S&P 500 since the late 1920s is about 6.6%.
Why are asset classes useful?
Financial advisors focus on asset classes to help diversify portfolios and maximize returns. Different asset classes reflect different risk and return characteristics, performing differently in various market environments.
The Bottom Line
Asset classes are groups of investments with similar characteristics and governed by the same rules and regulations. Equities, fixed income, commodities, and real estate are common examples of asset classes. By diversifying portfolios with asset classes that have low correlation, investors can reduce risk and enhance their chances of positive returns.



