Valuing a Company Business Valuation Defined With 6 Methods
Valuing a Company: Business Valuation Defined With 6 Methods
We and our 1609 partners store and/or access information on a device, such as unique IDs in cookies to process personal data. You may accept or manage your choices by clicking below, including your right to object where legitimate interest is used, or at any time in the privacy policy page. These choices will be signaled to our partners and will not affect browsing data.
We and our partners process data to provide:
Store and/or access information on a device. Use limited data to select advertising. Create profiles for personalised advertising. Use profiles to select personalised advertising. Create profiles to personalise content. Use profiles to select personalised content. Measure advertising performance. Measure content performance. Understand audiences through statistics or combinations of data from different sources. Develop and improve services. Use limited data to select content. List of Partners (vendors)
What Is a Business Valuation?
A business valuation, also known as a company valuation, is the process of determining the economic value of a business. During the valuation process, all areas of a business are analyzed to determine its worth and the worth of its departments or units.
A company valuation can be used to determine the fair value of a business for a variety of reasons, including sale value, establishing partner ownership, taxation, and even divorce proceedings. Owners will often turn to professional business evaluators for an objective estimate of the value of the business.
Key Takeaways
– Business valuation determines the economic value of a business or business unit.
– Business valuation can be used to determine the fair value of a business for a variety of reasons, including sale value, establishing partner ownership, taxation, and even divorce proceedings.
– Several methods of valuing a business exist, such as its market cap, earnings multipliers, or book value, among others.
The Basics of Business Valuation
The topic of business valuation is frequently discussed in corporate finance. Business valuation is typically conducted when a company is looking to sell all or a portion of its operations or looking to merge with or acquire another company. The valuation of a business is the process of determining the current worth of a business, using objective measures, and evaluating all aspects of the business.
A business valuation might include an analysis of the company’s management, its capital structure, its future earnings prospects, or the market value of its assets. The tools used for valuation can vary among evaluators, businesses, and industries. Common approaches include a review of financial statements, discounting cash flow models, and comparing similar companies.
Valuation is also important for tax reporting. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) requires that a business is valued based on its fair market value. Some tax-related events such as sale, purchase, or gifting of shares of a company will be taxed depending on valuation.
Estimating the fair value of a business is an art and a science; there are several formal models that can be used, but choosing the right one and the appropriate inputs can be somewhat subjective.
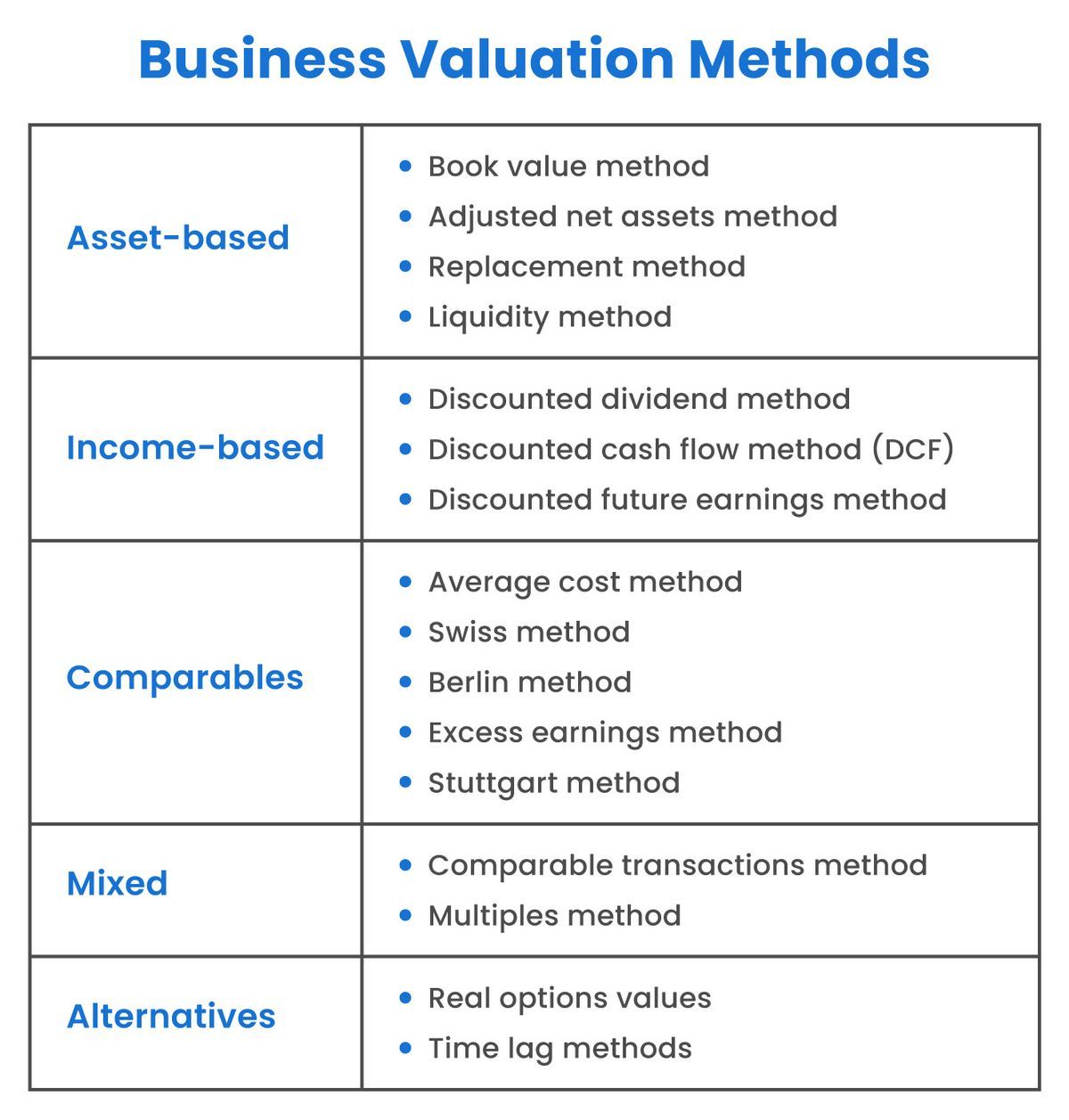
Methods of Valuation
There are numerous ways a company can be valued. You’ll learn about several of these methods below.
1. Market Capitalization
Market capitalization is the simplest method of business valuation. It is calculated by multiplying the company’s share price by its total number of shares outstanding. For example, as of January 3, 2018, Microsoft Inc. traded at $86.35. With a total number of shares outstanding of 7.715 billion, the company could then be valued at $86.35 x 7.715 billion = $666.19 billion.
2. Times Revenue Method
Under the times revenue business valuation method, a stream of revenues generated over a certain period of time is applied to a multiplier which depends on the industry and economic environment. For example, a tech company may be valued at 3x revenue, while a service firm may be valued at 0.5x revenue.
3. Earnings Multiplier
Instead of the times revenue method, the earnings multiplier may be used to get a more accurate picture of the real value of a company, since a company’s profits are a more reliable indicator of its financial success than sales revenue is. The earnings multiplier adjusts future profits against cash flow that could be invested at the current interest rate over the same period of time. In other words, it adjusts the current P/E ratio to account for current interest rates.
4. Discounted Cash Flow (DCF) Method
The DCF method of business valuation is similar to the earnings multiplier. This method is based on projections of future cash flows, which are adjusted to get the current market value of the company. The main difference between the discounted cash flow method and the profit multiplier method is that it takes inflation into consideration to calculate the present value.
5. Book Value
This is the value of shareholders’ equity of a business as shown on the balance sheet. The book value is derived by subtracting the total liabilities of a company from its total assets.
6. Liquidation Value
Liquidation value is the net cash that a business will receive if its assets were liquidated and liabilities were paid off today.
This is by no means an exhaustive list of the business valuation methods in use today. Other methods include replacement value, breakup value, asset-based valuation, and many more.
Accreditation in Business Valuation
Maintaining the ABV credential also requires those who hold the certification to meet minimum standards for work experience and lifelong learning. Successful applicants earn the right to use the ABV designation with their names. In Canada, Chartered Business Valuator (CBV) is a professional designation for business valuation specialists. It is offered by the Canadian Institute of Chartered Business Valuators (CICBV).