Value-Added Network VAN Definition How It Works and Purpose
Contents
Value-Added Network (VAN): Definition, How It Works, and Purpose
What Is a Value-Added Network (VAN)?
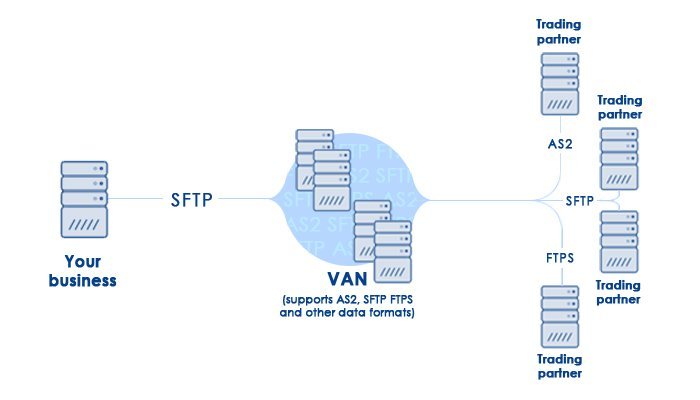
A value-added network (VAN) is a private, hosted service that provides companies with a secure way to send and share data with counterparties. VANs were common for electronic data interchange (EDI) between companies. As the internet created competition, VANs expanded their services to include message encryption, secure email, and management reporting.
VANs simplify communications by reducing the number of parties involved. They act as intermediaries between business partners that share standards-based or proprietary data. VANs have audit capabilities to validate the exchanged data before transferring it to the next party. VANs are also known as added-value networks or turnkey communications lines.
Key Takeaways
- VANs are used for electronic data interchanging between companies.
- VANs make the communications process easier with fewer parties involved.
- VANs are important for managing supply chains.
How a Value-Added Network (VAN) Works
Value-added networks are used by large companies for efficient supply chain management with suppliers, industry consortiums, or telecommunications companies. VANs operate in a mailbox setting, where a company sends a transaction to a VAN, and the VAN places it in the receiver’s mailbox. The receiver contacts the VAN to pick up the transaction and sends its own transaction.
The system is similar to email, but used for standardized structured data instead of unstructured text.
VANs in the Internet Era
The ubiquity of the Internet has reduced the appeal of VANs due to cost considerations. Moving data over the Internet is often more cost-effective than paying monthly fees and per-character charges in typical VAN contracts. However, VANs still serve specific industry verticals, such as healthcare, retail, and manufacturing, which have unique data integrity and security concerns.
VANs simplify communications by allowing companies to interact with fewer parties. The exchanged data can be directly formatted for the receiving organization’s software application. This ensures faster commerce and reduces human errors from manual data entry.
VANs also provide visibility tools, showing the status of data delivery and corresponding workflows. This allows companies to coordinate activities through the system, eliminating the need for phone calls and emails. VANs are not only efficient and accurate but also save costs by eliminating the need for human data-entry professionals.
To remain relevant, VANs now offer services beyond EDI exchange and retrieval. They provide automatic backups of EDI data, flexible access via secure web portals, and unlimited data pricing packages.



