Unitranche Debt Financing How These Hybrid Loans Work
Unitranche Debt: How These Hybrid Loans Work
What Is Unitranche Debt?
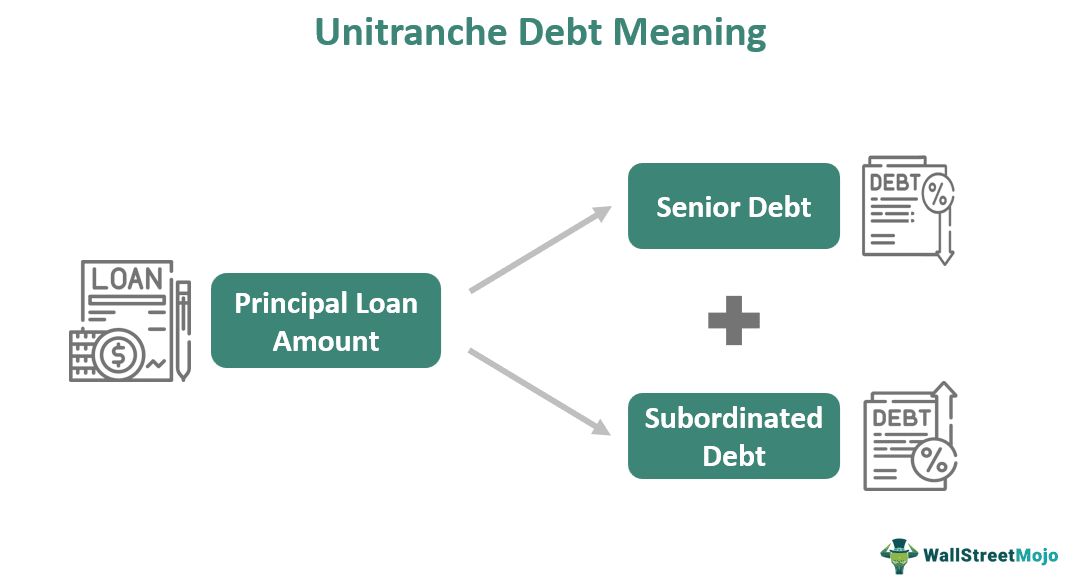
Unitranche debt represents a hybrid loan structure that combines senior debt and subordinated debt into one loan. This allows banks to compete against private debt funds. The borrower pays an interest rate that falls between the rates that each type of loan would individually command.
Unitranche debt is commonly used in institutional funding deals. It allows the borrower to get funding from multiple parties, resulting in decreased costs, greater fundraising, and faster acquisitions.
Key Takeaways
– Unitranche debt combines different loans into one, with an interest rate for the borrower that sits between the highest and lowest rate on the individual loans.
– It is commonly used in institutional funding deals, providing access to funds from multiple parties.
– It is comparable to syndicated debt, as both loans offer an average cost of debt to the issuer.
Understanding Unitranche Debt
Unitranche debt deals can be structured in various ways, with a focus on priority repayment levels for borrowers. Levels of risk can vary, with borrowers agreeing to different priority levels for repayment in case of default.
Unitranche debt may be compared to syndicated debt, as both are structured under an issuance agreement that provides an average cost of debt to the issuer.
Important: Unitranche debt collects funding from multiple participants with varying term structures.
Structured unitranche debt divides the debt vehicle into tranches, each with its own class designation. The terms of each tranche, including interest payments, rate, duration, and seniority, are determined by underwriters.
Seniority is the primary factor influencing the terms of each tranche. The tranches can be identified using class level names, such as the year of issuance followed by a letter.
Underwriters structure the tranches by seniority, with the lowest risk tranches having the highest seniority. These tranches are also known as secured tranches. Each tranche will have differing levels of seniority if the issuer defaults.
Some unitranche vehicles may also have rated tranches to support marketing and disclosure of tranche sales. Underwriters can customize tranches with provisions such as call rights, full repayment at principal, and floating or fixed rates.
Unitranche Debt vs. Syndicated Loan
In some cases, a syndicated loan may be considered a type of unitranche debt. Both involve multiple lenders and underwriters. However, syndicated loans are typically less complex in their structuring than unitranche debt.



