Middle Office Definition and Function in Financial Services Firms
Betsy’s career in international finance has evolved into journalism, drawing from her experience in academia and professional services.
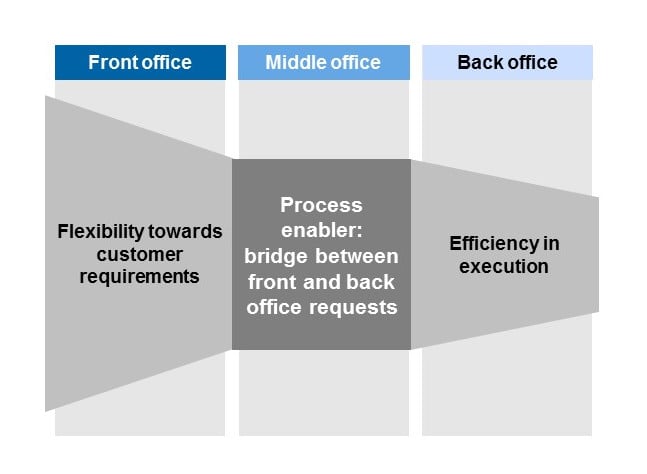
The middle office is a department in financial services companies, investment banks, or hedge funds that sits between the front and back office. It manages risk, calculates profits and losses, and is responsible for information technology (IT).
Key takeaways:
– The middle office tracks and processes deals made by the front office before being reconciled by the back office.
– It is responsible for risk management and a firm’s IT.
– The middle office originated from the increasing complexity of financial transactions.
In a financial services company, there are three parts: the front office (including sales personnel and corporate finance), the middle office (managing risk and IT resources), and the back office (providing administrative support and payment services). The middle office utilizes resources from both the front and back offices.
Middle and back office jobs do not directly generate revenue but are crucial for managing risk and ensuring accurate transactions. They are considered essential to a company’s infrastructure.
Initially, responsibilities between the front and back office personnel were divided, where the front office included salespeople, traders, and deal makers, while clerical work was done in the back office. As transactions and technology became more complex, the middle office emerged, requiring employees with at least a bachelor’s degree, and an increasing number with an MBA or master’s degree in technology.
On job sites, financial services companies typically list these positions as "middle office" opportunities.
Requirements of the middle office involve accurately booking, processing, and paying for deals negotiated by the front office. This includes managing International Swap Dealers Association (ISDA) agreements, tracking profits and losses, and ensuring completion of compliance documents. Some firms have legal support teams specialized in middle office functions.
In terms of information technology, middle office personnel are responsible for ensuring operational paying and receiving functions, designing software for implementing trading strategies, and managing contracted software systems like Bloomberg and Reuters 3000. They support both the front and back office, ensuring constant capture and monitoring of essential market data.
In recent years, financial services companies have outsourced back-office functions overseas to reduce costs. Since the financial crisis of 2008, some middle office functions have also been relocated offshore. Target countries for these outsourced jobs often have a highly-educated population with strong English language skills but a lower pay scale. Popular destinations include Ireland and India.