What Are Accounting Policies and How Are They Used With Examples
Contents
- 1 What Are Accounting Policies and How Are They Used?
- 1.1 What Are Accounting Policies?
- 1.2 How Accounting Policies Are Used
- 1.3 Example of an Accounting Policy
- 1.4 What Is the Difference Between Accounting Policies and Principles?
- 1.5 What Are Some Examples of Accounting Policies?
- 1.6 What Is the Difference Between Conservative and Aggressive Accounting?
- 1.7 The Bottom Line
What Are Accounting Policies and How Are They Used?
What Are Accounting Policies?
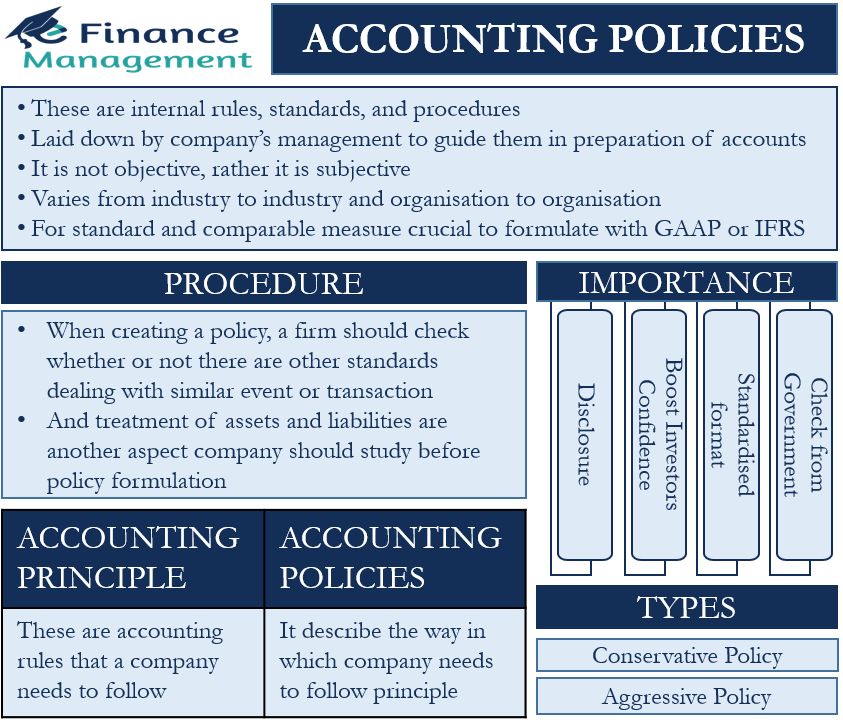
Accounting policies are specific procedures implemented by a company’s management team to prepare financial statements. They include accounting methods, measurement systems, and procedures for presenting disclosures. Accounting policies differ from accounting principles, as principles are the accounting rules and policies are a company’s way of adhering to those rules.
Key Takeaways
- Accounting policies are procedures that companies use to prepare financial statements.
- Unlike accounting principles, which are rules, accounting policies are the standards for following those rules.
- Accounting policies may be used to manipulate earnings legally.
- A company’s choice in accounting policies indicates the management’s approach to reporting earnings.
- Accounting policies need to adhere to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP).
How Accounting Policies Are Used
Accounting policies are standards that govern how a company prepares financial statements. They deal with complicated accounting practices such as depreciation methods, recognition of goodwill, preparation of research and development (R&D) costs, inventory valuation, and the consolidation of financial accounts. While these policies may differ between companies, they must conform to generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) and/or international financial reporting standards (IFRS).
Accounting principles provide a framework for companies to operate within, but the specific policies a company chooses are essential due to the flexibility in accounting principles. Investors should consider a company’s accounting policies to assess the quality of earnings, as they signal whether the management is conservative or aggressive in reporting earnings. External auditors should also review a company’s policies to ensure they conform to GAAP.
Important
Company management can select accounting policies advantageous to their financial reporting, such as choosing an inventory valuation method.
Example of an Accounting Policy
Accounting policies can be used to manipulate earnings legally. For example, companies can value inventory using average cost, first in first out (FIFO), or last in first out (LIFO) methods. Under the average cost method, the weighted average cost of all inventory produced or acquired in the accounting period is used to determine the cost of goods sold (COGS). Under the FIFO method, the cost of the inventory produced or acquired first is considered sold. Under the LIFO method, the cost of the inventory produced last is considered sold.
In periods of rising inventory prices, companies can use these accounting policies to increase or decrease earnings. For instance, a manufacturing company buys inventory at $10 per unit for the first half of the month and $12 per unit for the second half, purchasing a total of 10 units at $10 and 10 units at $12. It sells a total of 15 units for the entire month.
If the company uses FIFO, the cost of goods sold is: (10 x $10) + (5 x $12) = $160. If it uses the average cost, the cost of goods sold is: (15 x $11) = $165. If it uses LIFO, the cost of goods sold is: (10 x $12) + (5 x $10) = $170. Therefore, using the FIFO method minimizes the cost of goods sold and increases earnings in periods of rising prices.
What Is the Difference Between Accounting Policies and Principles?
While accounting principles are standardized rules set forth by governing bodies, accounting policies are the methods or guidelines used by management to adhere to the rules and generate financial statements.
In the United States, generally accepted accounting principles (GAAP) are the accounting standards accepted by the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Accounting principles allow for management discretion, and that is where accounting policies come into play.
What Are Some Examples of Accounting Policies?
Accounting policies appear in business when accounting principles allow leeway in applying the rules to a situation. Situations involving management discretion include:
- Valuation of inventory
- Valuation of investments
- Valuation of fixed assets
- Depreciation methods
- Costs of research and development (R&D)
- Translation of foreign currency
What Is the Difference Between Conservative and Aggressive Accounting?
Conservative accounting uses policies that tend to understate revenue and/or overstate expenses. Aggressive accounting uses policies that tend to overstate revenue and/or understate expenses.
A company using conservative accounting policies will have lower earnings in the current year, while a company using aggressive accounting policies will show better financial performance. Conservative accounting policies tend toward better financial performance in the long run, while aggressive accounting policies may lead to a decline in financial performance over time.
The Bottom Line
Accounting policies differ from accounting principles, as principles are the accounting rules and policies are a company’s way of adhering to those rules. A company’s management team can choose specific accounting policies advantageous to its financial reporting, which can influence the appearance of financial performance in a given year.