Mobile Banking

Mobile Banking
Mobile banking is the act of making financial transactions on a mobile device. This activity can be as simple as a bank sending fraud or usage activity to a client’s cell phone or as complex as a client paying bills or sending money abroad. Advantages of mobile banking include the ability to bank anywhere and at any time. Disadvantages include security concerns and limited capabilities compared to banking in person or on a computer.
Understanding Mobile Banking
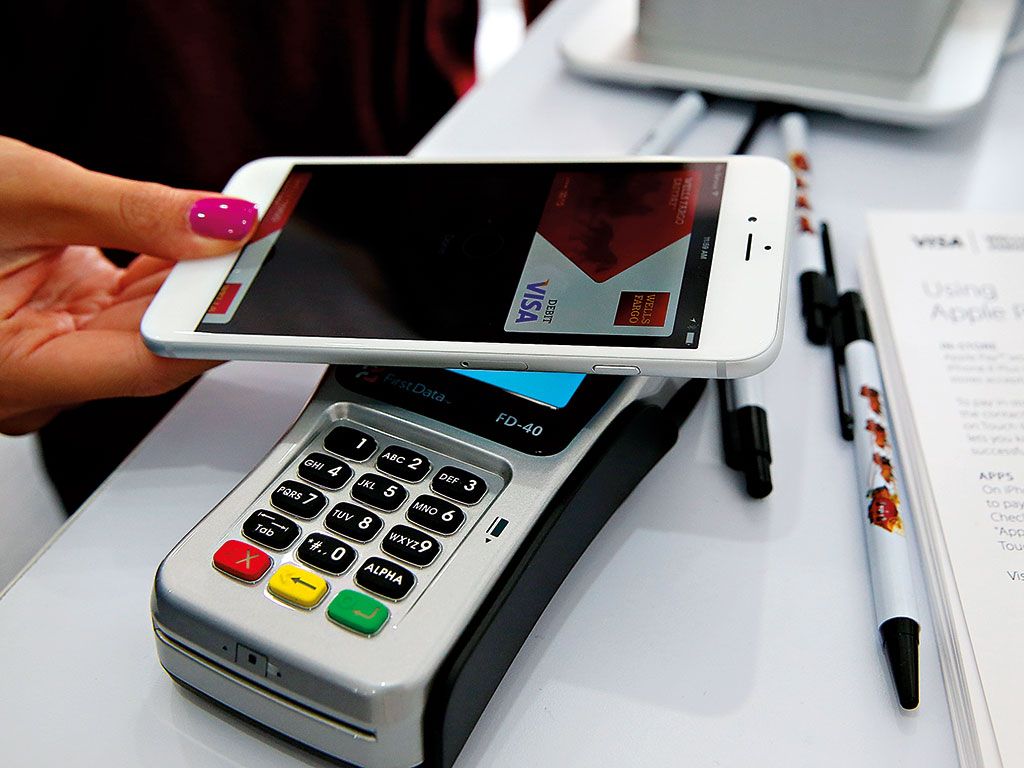
Mobile banking is convenient in today’s digital age with many banks offering impressive apps. The ability to deposit a check, pay for merchandise, transfer money to a friend, or find an ATM instantly are reasons why people use mobile banking. However, establishing a secure connection before logging into a mobile banking app is important to protect personal information from being compromised.
Mobile Banking and Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is increasingly important in mobile banking operations. It encompasses measures to keep electronic information private and avoid damage or theft. Three main types of cyber attacks can occur:
1. Backdoor attacks, where thieves exploit alternate methods of accessing a system without the usual authentication means.
2. Denial-of-service attacks, which prevent the rightful user from accessing the system.
3. Direct-access attacks by bugs and viruses, which copy or modify a system’s information.
Financial advisors can take the following steps to protect clients against cyber attacks:
1. Educate clients about the importance of strong, unique passwords and using a password manager for added security.
2. Never access client data from a public location and ensure the connection is always private and secure.
Mobile Banking and Remittances
Remittances are funds that an expatriate sends to their country of origin via wire, mail, or mobile banking. These peer-to-peer transfers of funds across borders have economic significance for many receiving countries. The World Bank and the Gates Foundation estimate that remittances to developing countries amounted to $529 billion in 2018, up 9.6% from the previous record high of $486 billion in 2017.