What Are Asset Sales Definition How It Works and Taxation
Asset Sales: Definition, How It Works, and Taxation
Asset sales occur when a bank or firm sells its receivables to another party. These transactions are executed to mitigate asset-related risk, obtain free cash flows, or meet liquidation requirements.
Asset sales affect a company’s net income.
Key Takeaways:
– In an asset sale, a firm sells its actual assets, either tangible or intangible.
– The seller retains legal ownership of the company but has no further recourse to the sold assets.
– The buyer assumes no liabilities in an asset sale.
– Buyers prefer asset sales for tax benefits, whereas sellers prefer stock sales.
How Asset Sales Work
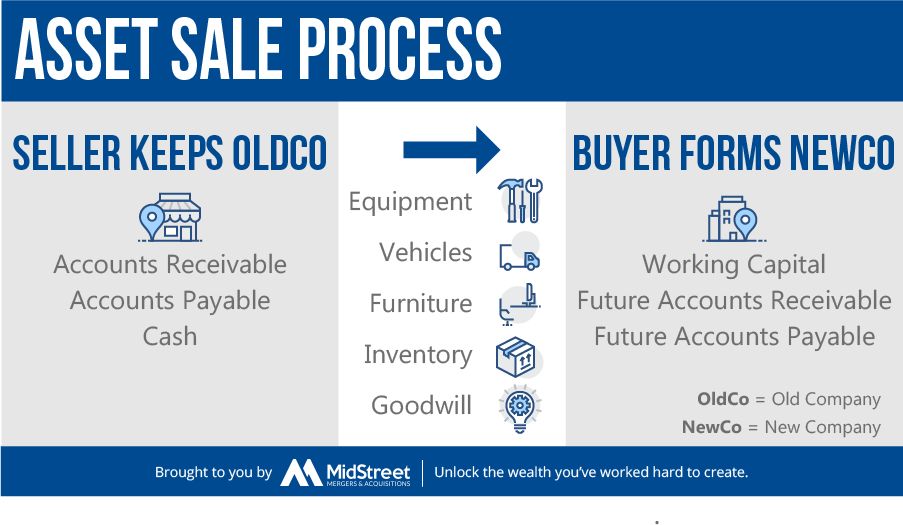
Asset sales involve the actual assets of a business, different from shares of stock. These can be complex transactions from an accounting perspective. Accounts receivable are kept on the balance sheet. An asset sale is classified as such when the buyer gains control of the property after payment.
The buyer has no further recourse to the assets after the sale. Allowing recourse would classify the transaction as financing, which doesn’t provide increased free cash flows.
For banks, asset sales are often done through the sales of individual loans or pools of whole loans, or through the securitization of receivables. For other companies, assets can be tangible (inventory, real estate, equipment, investments, working capital, or a subsidiary/division) or intangible (patents, trademarks, copyrights, goodwill).
When a government performs an asset sale, it is known as disinvestment.
Special Considerations
In an asset sale, a business can choose what it sells. The buyer purchases individual assets, while the seller retains ownership of the legal entity. The buyer may create a new company or use an existing subsidiary to acquire the assets, along with management and contracts. Asset sales carry less risk for buyers since liabilities and contingent expenses remain the seller’s responsibility.
Buyers prefer asset sales, while sellers prefer stock sales. However, if a business is unincorporated, an asset sale may be the only option.
Tax Implications of Asset Sales
Asset sales offer tax benefits to buyers. They allow buyers to step up the tax basis in acquired assets, resulting in considerable tax breaks. For sellers, asset sales often generate higher income taxes. Some intangible assets, like goodwill, are taxed at capital gains rates, while other assets face higher ordinary income tax rates.
Additionally, if the assets sold are held in a "C" corporation, double taxation is a concern. The corporation is first taxed when selling the assets to the buyer, and the shareholders are taxed again when the sales proceeds are distributed.
With stock sales, all proceeds are taxed at the lower capital gains rate. In some cases, if the business is taking a loss, the entire price may be tax-free.