Transaction Exposure Definition Example Hedging Strategies
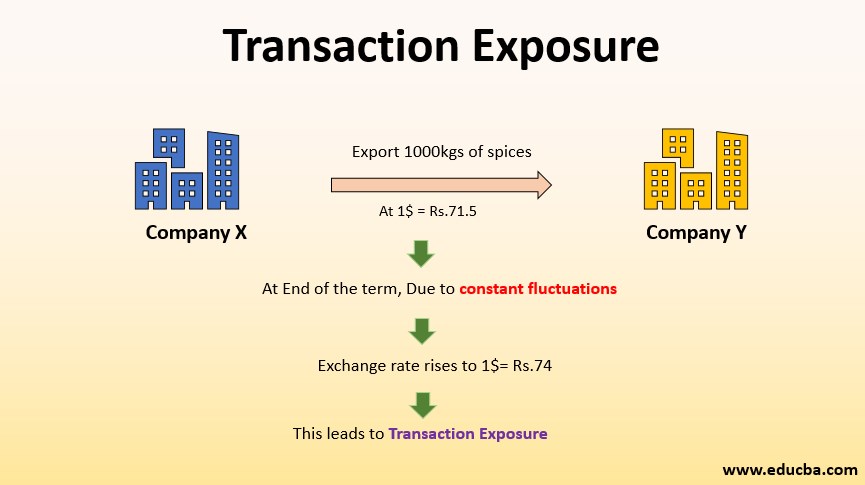
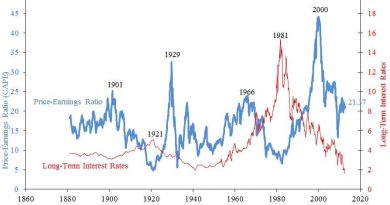
Transaction exposure is the uncertainty that international trade businesses face due to currency exchange rate fluctuations. This risk can result in significant capital losses for these businesses. Transaction exposure is also referred to as translation exposure or translation risk.
Key takeaways:
– Transaction exposure is the uncertainty faced by companies in international trade due to currency fluctuations.
– A high level of exposure to exchange rates can lead to major losses, but hedging strategies can be used to mitigate these risks.
– Transaction exposure generally impacts only one side of a transaction, specifically the business that completes the transaction in a foreign currency.
Understanding transaction exposure:
Transaction exposure is typically one-sided, affecting only the business that completes a transaction in a foreign currency. The entity paying or receiving a bill using its home currency is not exposed to the same risk. If a buyer agrees to purchase a product using foreign currency, the risk arises if that currency appreciates, resulting in increased costs for the goods. The risk of exchange rate fluctuations increases with time between the agreement and contract settlement.
Combating transaction exposure:
One way to limit exposure to changes in exchange rates is through hedging strategies such as currency swaps or futures contracts. These strategies allow a company to lock in a currency exchange rate for a specific period and reduce translation risk. Additionally, companies can request that clients pay for goods and services in the currency of the company’s home country, shifting the risk of local currency fluctuation to the client.
Example of transaction exposure:
Consider a scenario where a US-based company intends to purchase a product from a German company and agrees to use the euro as the payment currency. The exchange rate at the start of negotiations is 1 euro to 1.5 US dollars (USD). If the exchange rate changes before the sale is finalized, it exposes the US company to transaction exposure. When making the payment, the exchange rate may have shifted to a more favorable or less favorable rate. However, the German company does not experience transaction exposure since the deal was in its local currency.
In conclusion, transaction exposure poses a risk to businesses involved in international trade due to currency exchange rate fluctuations. Implementing hedging strategies and requesting payments in the company’s home currency can help mitigate these risks.