Market Exposure Definition Measurement Types Risk Strategies
Market Exposure: Definition, Measurement, Types, Risk Strategies
What Is Market Exposure?
Market exposure refers to the funds or percentage invested in a security, market sector, or industry. It is usually expressed as a percentage of the portfolio, such as 10% of a portfolio in the oil and gas sector or $50,000 in Tesla stock.
Market exposure represents the amount an investor can lose from unique risks associated with an investment or asset class. It measures and balances risk in a portfolio. Too much exposure to one area may indicate a need for diversification.
Key Takeaways
– Market exposure is the proportion of assets tied up in securities or markets.
– Market exposure can be subdivided to gain insight into risks across different markets.
– Measuring and balancing market exposure is crucial for managing total risk.
Understanding Market Exposure
Market exposure describes the risk and reward potential within an investment portfolio. It measures the degree of exposure to potential loss in specific assets.
Market exposure can be reduced by diversifying assets across different classes, regions, or industries. Higher market exposure means greater market risk in that investment area. Concentration in one area can lead to significant losses.
Market Exposure by Investment Type
Investments can be segmented based on the asset class involved. For example, a portfolio with 20% bonds and 80% stocks has an 80% market exposure to stocks. Performance of stocks will have a greater impact on returns.
Market Exposure by Region
Market exposure can also be examined by geographic location. Investors may separate domestic and foreign investments, or further divide foreign markets by regions or emerging markets.
For example, a portfolio could allocate 50% to domestic and 50% to foreign stocks. Foreign holdings can be divided to show 30% in Asian markets and 20% in European markets. The Asian segment can be further divided into developed and emerging markets.
Market Exposure by Industry Segment
Investments can be divided by industry or economic sector. For example, an 80% market exposure to stocks may include 30% in the health care sector, 25% in technology, 20% in financial services, 15% in defense, and 10% in energy.
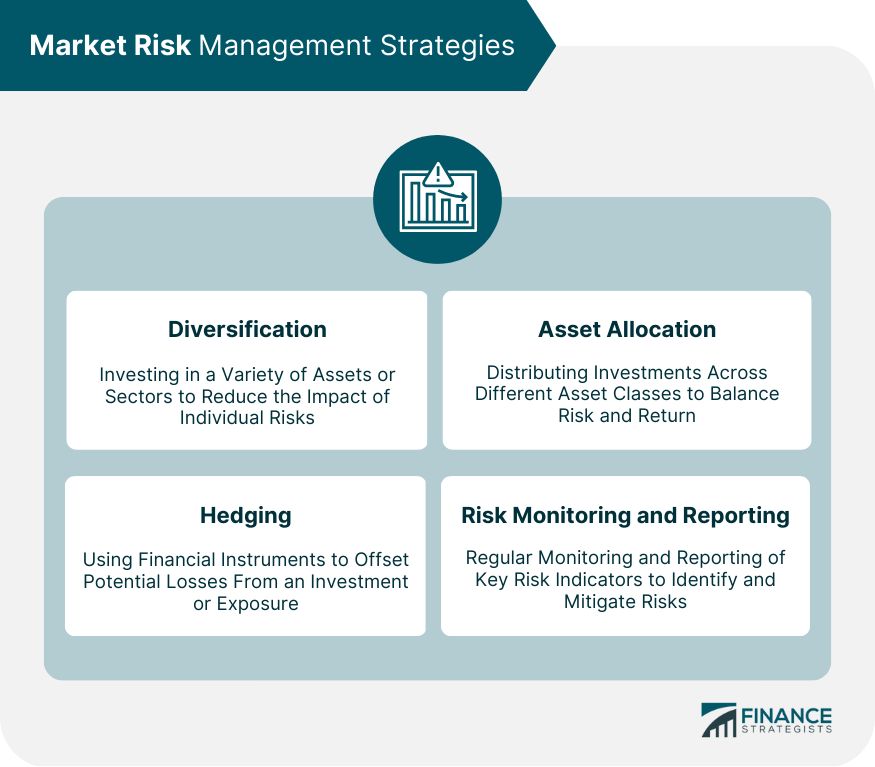
Exposure, Diversification, and Risk Management
Considering exposure to particular securities, markets, or sectors is important for asset allocation. Diversification reduces market exposure risks while increasing returns. A portfolio with both stocks and bonds has less risk than one with only stocks.
Reducing high market exposure can be done by selling holdings in specific sectors. For example, selling 50% of health care holdings reduces exposure to 15% due to industry changes brought by new regulations.