Trading Plan Definition How It Works Rules and Examples
Trading Plan: Definition, How It Works, Rules, and Examples
What Is a Trading Plan?
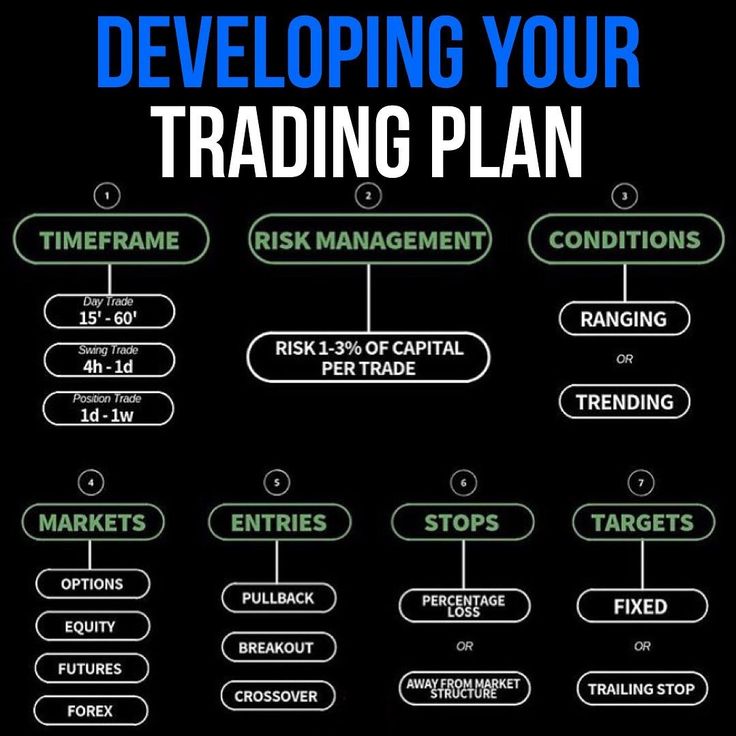
A trading plan is a systematic method for identifying and trading securities that considers variables such as time, risk, and investor objectives. It outlines how a trader will find and execute trades, including under what conditions they will buy and sell securities, position sizing, managing open positions, eligible securities, and other trading and non-trading rules.
Key Takeaways:
– A trading plan is a roadmap for trading and should guide all trading decisions.
– The plan is written down and followed, only altered if it is found not to work or can be improved.
– A basic trading plan includes entry and exit rules, risk management, and position sizing. Additional rules can be added at the trader’s discretion.
Understanding the Trading Plan
Trading plans can be customized based on personal goals and objectives. They can be lengthy and detailed for active day traders or simple for investors making automatic investments each month.
Automatic Investing and Simple Trading Plans
Investors can automate investments at regular intervals, but it should still be based on a written plan. This prepares them for different market scenarios, such as losses or market volatility.
For example, a 30-year old may deposit $500 each month into a mutual fund. If they find their holdings have decreased after three years, the trading plan outlines how to exit the positions.
Tactical or Active Trading Plans
Short-term and long-term investors may use tactical trading plans, which are more detailed than automatic investing. These plans specify entry criteria, exit rules for profit and loss, capital allocation, and position sizing. Additional rules may be added to control when it is acceptable to trade.
Altering a Trading Plan
Trading plans should be well-thought-out and not changed due to losses or rough patches. They should only be altered if a better way of trading or investing is discovered.
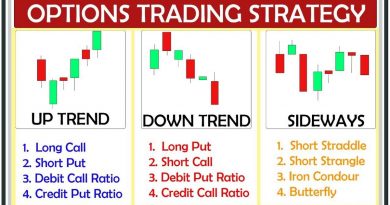
Example of a Trading Plan—Position Sizing and Risk Management
A trading plan should outline what, when, and how to buy and sell securities, as well as how to manage risk. It may include rules for position sizing based on account balance, whether leverage can be used, trading correlated assets, and trading restrictions.
The risk management section of the trading plan is customized by the trader to manage risk based on their objectives and risk tolerance.