What Are Fundamentals Types Common Analysis Ratios and Example
Fundamentals are the basic information that contributes to the financial or economic well-being of a company, security, or currency. Qualitative information includes elements that cannot be directly measured, while quantitative analysis uses mathematics and statistics to understand and predict asset movements.
Key Takeaways:
– Fundamentals provide a method to set the financial value of a company, security, or currency.
– Fundamental analysis includes qualitative and quantitative information.
– Macroeconomic fundamentals affect the entire economy.
– Microeconomic fundamentals focus on smaller segments of the economy.
– Fundamentals for businesses include profitability, revenue, assets, liabilities, and growth potential.
Understanding Fundamentals:
Fundamentals represent the primary characteristics and financial data necessary to determine the stability and health of an asset. Analysts and investors examine fundamentals to estimate a worthwhile investment. Through fundamental analysis, you can calculate financial ratios to determine feasibility.
Fundamentals for National Economies:
Interest rates, GDP growth, trade balance surplus/deficits, and inflation levels are fundamental factors that affect a nation’s value.
Macroeconomic and Microeconomic Fundamentals:
Macroeconomic fundamentals encompass statistics regarding unemployment, supply and demand, growth, inflation, monetary or fiscal policy, and international trade. Microeconomic fundamentals focus on smaller segments, such as specific markets or sectors.
Fundamentals in Business:
Looking at overall management and financial statements helps evaluate a company’s fundamentals. Strong fundamentals indicate a viable framework or financial structure, while weak fundamentals may indicate issues in debt management, cost control, or organizational management.
Fundamental Analysis:
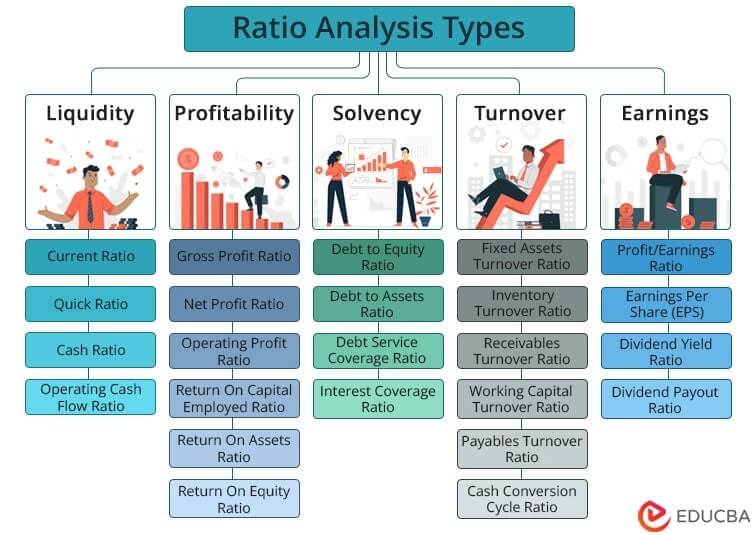
Investors evaluate a company’s fundamentals to compare its economic position relative to peers or the broader market. Fundamental analysis involves analyzing ratios, such as the debt-to-equity ratio, quick ratio, degree of financial leverage, price-to-earnings ratio, and DuPont analysis.
Real-World Example:
Microsoft and Apple had similar market caps but different fundamentals, which should be considered when choosing potential investments.
Difference Between Macroeconomic and Microeconomic Fundamentals:
Macroeconomic fundamentals relate to the global economy as a whole, while microeconomic fundamentals affect smaller segments.
Difference Between Quantitative and Qualitative Analysis:
Quantitative analysis uses mathematics and statistics, while qualitative analysis involves subjective elements and opinions.
Main Benefit of Fundamental Analysis in Business:
Fundamental analysis provides insights into a company’s value, risk, and growth potential, helping investors make informed decisions.
The Bottom Line:
Fundamentals refer to the qualitative and quantitative information that reflects a company’s financial and economic position. Fundamental analysis involves analyzing key ratios to draw conclusions on growth potential and financial health.



