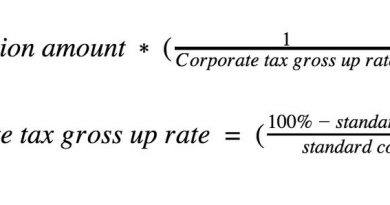What Are Contingencies and Contingency Plans Definition and Examples
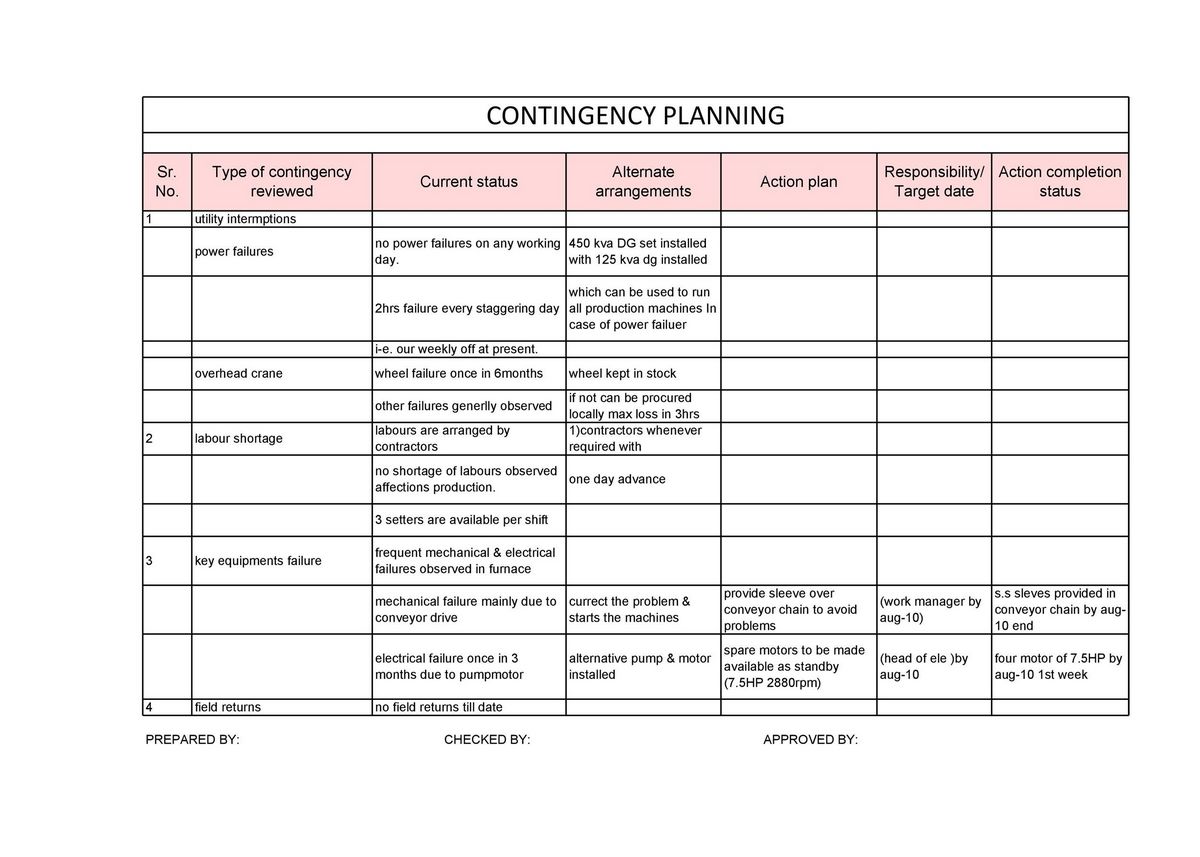
A contingency is a potential occurrence of a negative event in the future, such as an economic recession, natural disaster, fraudulent activity, terrorist attack, or a pandemic. Contingencies can be prepared for, but the nature and scope of such events are typically unknowable in advance. Companies and investors plan for contingencies through analysis and implementing protective measures.
Managers in finance attempt to identify and plan for possible contingencies using predictive models. They tend to err on the conservative side to mitigate risk, assuming slightly worse-than-expected outcomes.
A contingency plan includes arranging a company’s affairs to weather negative outcomes with the least distress possible.
Key Takeaways:
– A contingency is a potentially negative event, such as an economic recession or natural disaster.
– Companies and investors plan for contingencies through analysis and implementing protective measures.
– A thorough contingency plan minimizes loss and damage caused by an unforeseen negative event.
– Contingency plans can include the purchase of options or insurance for investment portfolios.
– Banks must set aside capital for negative contingencies to protect against losses.
To plan for contingencies, financial managers may recommend setting aside reserves of cash so that the company has strong liquidity, even during a period of poor sales or unexpected expenses. Managers may also seek to proactively open credit lines while the company is in a strong financial position to ensure access to borrowing in less favorable times. Contingency plans typically include insurance policies that cover losses during and after a negative event.
However, insurance policies may not cover all costs or scenarios. For example, business interruption insurance usually doesn’t cover pandemics. As a result, the government may need to provide financial relief, as seen with the Coronavirus Aid, Relief, and Economic Security (CARES) Act.
In addition, insurance companies might limit coverage or put exclusions in place for acts of God, such as a flood or earthquake. Insurance cannot replace lost customers due to events like a data breach.
Therefore, businesses need to establish contingency plans to minimize lost revenue and increased costs when operations are disrupted. Business consultants are often hired to ensure contingency plans consider a large number of possible scenarios and provide advice on execution.
Types of Contingency Plans:
– Protecting Assets: Contingency plans might involve purchasing insurance policies that pay benefits if a particular contingency occurs.
– Investment Positions: Investors protect themselves from contingencies that could lead to financial losses related to investing. They might employ hedging strategies, stop-loss orders, or options strategies.
– Contingent Immunization: Contingent immunization is a type of contingency plan used in fixed-income investing. It involves switching to a defensive position if the portfolio drops below a predetermined value.
– Business Continuity and Recovery: Companies need to plan for disasters and ensure that business operations can continue during and after an event. This often involves a business continuity plan and investing in technology for remote work.
Cybersecurity is also an important consideration in contingency planning, as cybercriminals often try to exploit crises to hack into a company’s systems.
In addition to protecting against external events, contingency plans should address the loss or destruction of intellectual property, operational mishaps, theft, and fraud. A company should also have an emergency public relations response and procedures for reorganizing after a negative event.
Benefits of a Contingency Plan:
– Minimizing loss and damage caused by an unforeseen negative event.
– Reducing the risk of a public relations disaster.
– Allowing the company to keep operating during a negative event.
– Obtaining better insurance rates and credit availability.
Banks are required to perform stress tests to determine if they have enough capital to survive negative economic events. Regulations dictate the percentage of capital reserves banks must have in relation to risk-weighted assets. These reserves protect against potential losses during negative scenarios.
Overall, businesses, governments, and individuals must design plans that consider contingencies to limit the damage caused by negative events.