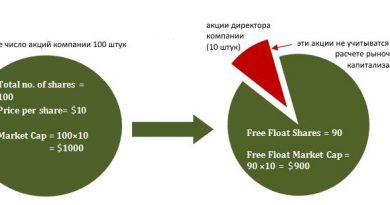
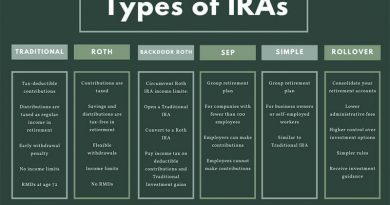
Welfare Definition Different Types Who Qualifies

Contents
- 1 Welfare: Definition, Types, and Qualifications
- 1.1 What Is Welfare?
- 1.2 How Welfare Works
- 1.3 Special Considerations
- 1.4 Types of U.S. Welfare Programs
- 1.5 Who Qualifies for Welfare
- 1.6 What Is Considered Welfare?
- 1.7 What Makes You Eligible for Welfare?
- 1.8 What Can Welfare Help Me With?
- 1.9 What Welfare Programs Does the United States Have?
- 1.10 What Is Social Welfare?
- 1.11 The Bottom Line
Welfare: Definition, Types, and Qualifications
What Is Welfare?
Welfare refers to government programs providing financial or other aid to individuals or groups who cannot support themselves. These programs are funded by taxpayers to help people cope with financial stress. Welfare goals include promoting work, education, and a higher standard of living.
Key Takeaways
- Welfare refers to government-sponsored assistance programs for individuals and families in need.
- Welfare programs are funded through federal taxation.
- The federal government provides grants to states through the Temporary Assistance for Needy Families program.
- Benefits eligibility is based on factors such as income levels and family size.
- Welfare beneficiaries receive monthly SNAP payments through an EBT card.
How Welfare Works
Welfare systems provide assistance in healthcare, food, unemployment compensation, housing, and child care. Each state determines eligibility based on financial status and minimum acceptable levels. Factors for eligibility include family size, income levels, and disabilities.
Different states may have similar welfare systems with varying names and qualifications due to differences in poverty lines and cost of living.
Welfare recipients usually receive free or discounted goods and services, but they must prove their income falls below the federal poverty level (FPL). The FPL determines eligibility for subsidies or aid, with the current guidelines set at $14,580 for one person and $30,000 for a family of four in 2023.
Special Considerations
Welfare programs in the U.S. are aimed at supporting poor, developmentally challenged, and disadvantaged groups. Compared to other developed countries, the U.S. has fewer welfare programs with greater restrictions.
The history of welfare programs in the United States is complex and controversial. Past presidents created programs to address poverty. Welfare programs and assistance continue to evolve and expand under President Joe Biden’s leadership.
There are seven major welfare programs in America:
- Medicaid
- Supplemental Security Income (SSI)
- Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)
- Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP)
- Temporary Assistance to Needy Families
- Housing assistance
- Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
Grants from the federal government are not given directly to individuals or families in need. Any offers to help obtain these grants are scams.
Types of U.S. Welfare Programs
Medicaid
Medicaid provides health insurance to those with income below federal poverty standards and aging adults. Pregnant women, children, people with disabilities, and aging adults receive coverage under Medicaid.
Supplemental Security Income (SSI)
SSI offers public assistance to children and adults living with disabilities. Qualifying disabilities include blindness, neurological challenges, respiratory disease, and failure to thrive.
Supplemental Nutrition Assistance Program (SNAP)
SNAP, previously known as the Food Stamp Program, provides vouchers to low-income households to buy nutritious and low-cost foods.
Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP)
CHIP provides low-cost health care to children in households that do not qualify for Medicaid. It covers benefits like dental care and special needs assistance.
Temporary Assistance to Needy Families
Temporary Assistance to Needy Families requires recipients to find a job within two years to receive benefits. States receive federal grants to operate their own welfare programs.
Housing Assistance
Housing choice vouchers help low-income households, people with disabilities, and aging adults access affordable rental homes. These vouchers are funded by the U.S. Department of Housing and Urban Development.
Earned Income Tax Credit (EITC)
EITC provides tax breaks to low to moderate-income individuals and families.
Welfare vs. Entitlements
Entitlements are offered to all citizens without qualifications. Welfare programs have specific criteria. Examples of entitlements include Social Security income and Medicare.
Who Qualifies for Welfare
Government welfare primarily supports people with little to no income, aging adults, and those with disabilities. Eligible recipients must be legal citizens or permanent residents of the United States. Valid Social Security Numbers are required for applications.
Qualifications may vary by state, and desired outcomes on welfare depend on the circumstances that led to the application.
What Is Considered Welfare?
Welfare includes government programs providing financial or other assistance for housing, food, and healthcare based on specific guidelines.
What Makes You Eligible for Welfare?
Eligibility requirements vary for different welfare programs and often include income limits, citizenship, and family size.
What Can Welfare Help Me With?
Welfare programs help individuals and families secure housing, access healthcare, purchase food, provide financial assistance, and take advantage of tax breaks.
What Welfare Programs Does the United States Have?
Welfare programs in the U.S. include Medicaid, Supplemental Security Income, SNAP, CHIP, Temporary Assistance for Needy Families, housing assistance, and EITC.
What Is Social Welfare?
Social welfare provides assistance to individuals or families in need. The availability and amount of welfare vary by country, region, or state.
The Bottom Line
Welfare comprises government programs helping individuals and families with low income achieve a decent standard of living. These programs provide housing, food, medical care, and financial assistance. Their goal is to support people in need as they work towards financial stability.