Waiting Period Definition Types and Examples
Waiting Period: Definition, Types, and Examples
A waiting period, also known as a qualifying period, is the time before insurance coverage kicks in. Insurance policies, including homeowners insurance, auto insurance, and short-term disability, can have waiting periods. Companies with high turnover rates often use waiting periods. Some private health insurance plans have longer wait periods for cancer or maternity care.
How a Waiting Period Works
The waiting period or elimination period before the insured can make claims varies by insurer, policy, and type of insurance. Longer waiting periods may slightly reduce the cost of premiums. Different types of waiting periods exist in health insurance.
Employer waiting periods require employees to wait, such as three months, before receiving company-subsidized health services. Additional waiting periods may be imposed after enrollment.
Health Maintenance Organizations (HMO) have affiliation waiting periods. HIPAA regulates these periods and sets a maximum limit of two months (three months for late enrollees).
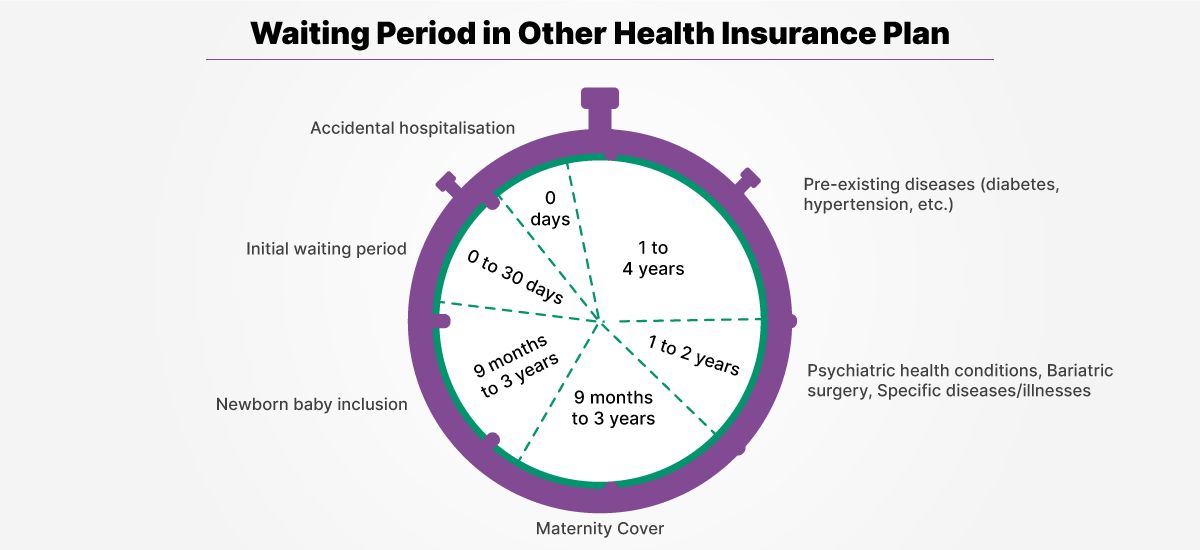
Pre-existing condition exclusion periods last from one to 18 months. They refer to health conditions an individual may have before enrolling in a health insurance plan. Coverage may be limited or excluded for pre-existing conditions, but previous uninterrupted insurance coverage can count towards this exclusion. Exemptions apply to those with at least one year of group health coverage at one job and a span of no more than 63 days.
Some private health insurance plans have long mandatory waiting periods for certain types of coverage:
– Cancer and cardiovascular care may require wait periods of up to two years.
– Maternity care waits can range from 10 to 12 months, but commonly range from 30 to 90 days.
– Dental care waiting periods are typically 6 to 12 months. Some insurance companies also impose restrictions on the frequency of specific dental treatments.
Policyholders should consider their ability to pay for expenses when choosing the length of the waiting period for a policy.
Types of Waiting Periods
Homeowner insurance wait periods usually last 30 to 90 days before coverage takes effect. After the waiting period, policyholders can file claims.
Some states may impose wait periods on other insurance products. For example, Texas enforces a 60-day wait on new auto insurance policies to assess risk profiles.
Short-term disability coverage can have wait periods as short as a few weeks but with higher premiums. Most short-term policies wait 30 to 90 days for coverage. Long-term disability wait periods range from 90 days to a year. During the probationary period, no benefits are payable. Social Security disability payments also have a five-month waiting period.
By minimizing redundant words and phrases, the text is now more concise and impactful while maintaining the original meaning.