Volumetric Production Payment VPP Meaning How it Works
Cierra Murry is an experienced banking consultant, loan signing agent, and arbitrator with over 15 years of expertise in financial analysis, underwriting, loan documentation, loan review, banking compliance, and credit risk management.
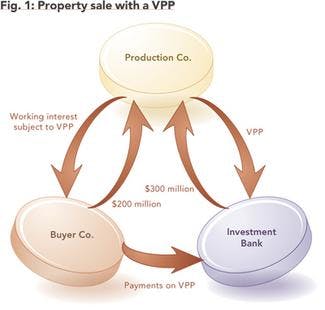
A Volumetric Production Payment (VPP) is a type of structured investment where the owner of an oil or gas interest sells or borrows money against a specific volume of production associated with the field or property. The investor or lender receives a monthly quota, often in raw output, which is then marketed by the VPP buyer or a specified percentage of the monthly production achieved at the property.
Buyers can include investment banks, hedge funds, energy companies, and insurance companies.
Key Takeaways:
– Volumetric production payments (VPPs) convert oil or gas production into a cash flow stream for investors.
– Investors or buyers of a VPP are typically financial institutions or energy companies guaranteeing future delivery of oil or gas.
– Sellers in a VPP are oilfield companies or drillers that monetize their capital investment while retaining ownership of their property.
VPPs are sometimes part of a pre-export financing (PFX) package where a financial institution advances funds based on proven volume of orders. The borrower, typically an oil producer, needs the funding to produce and supply oil and gas. The VPP is used to repay the borrowing under the PFX arrangement. The credit quality of PFX is usually better than other lending since the cash flow from the VPP is used to repay the PFX before other creditors.
The VPP buyer isn’t involved in the production of the end product. However, investors often hedge their expected receivables via the derivatives market to protect against commodity risk or lock in the expected profits.
A VPP deal allows the seller to retain full ownership of the property while monetizing some of their capital investment. This allows the producer to invest in capital upgrades or repurchase shares. If the owner sells a specific volume of production instead of borrowing against it, the money can be used to repay other debt.
VPP Deal Details:
– A VPP deal typically expires after a specified time or when a specific total volume is delivered.
– A VPP interest is considered a non-operating asset, similar to a royalty or loan repayment system.
– Under the royalty-payment structure, if the producer can’t meet the supply quota for a month, the unmet portion is made up for in the next cycle until the buyer is financially whole.
– Under the loan repayment structure, failure to make a payment is considered default.