Virtual Currency Definition Types Advantages Disadvantages

Virtual Currency: Definition, Types, Advantages & Disadvantages
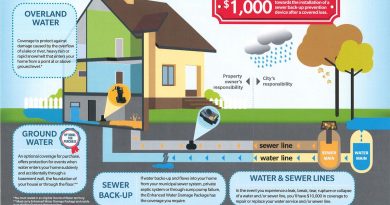
A virtual currency is a digital representation of value available electronically. It is stored and transacted through designated software, mobile, or computer applications. Transactions involving virtual currencies occur through secure networks or the internet. They are issued by private parties or groups of developers and are mostly unregulated.
Virtual currencies are a subset of digital currencies, such as cryptocurrencies and tokens, issued by private organizations. They can allow for faster transaction speeds, ease of use, and broad access. However, virtual currencies can be hacked and are not regulated, so users have no legal recourse if they are victims of an attack.
Key Takeaways:
– Virtual currencies are digital representations of value whose transactions occur online.
– All virtual currencies are digital currencies, but not all digital currencies are virtual currencies.
– Virtual currencies are issued by private organizations and are mostly unregulated.
– Virtual currencies strive to increase transaction speeds by removing intermediaries but are also susceptible to hacks and scams.
Understanding Virtual Currencies
Virtual currencies are a form of digital currency. They are issued by private parties, such as developers or organizations, and are intended only for online use—they do not have a physical incarnation like paper money. They differ from officially issued digital currency (CBDC).
Regulation
The term virtual currency came into existence in 2012 when the European Central Bank (ECB) defined it as "digital money in an unregulated environment, issued and controlled by its developers and used as a payment method among members of a specific virtual community." The European Union has also published a broad definition in its Markets In Crypto Assets (MiCA) regulation. The Internal Revenue Service (IRS) in the United States describes virtual currencies as "digital representations of value, other than the U.S. dollar or a foreign currency, that function as a unit of account, a store of value, and a medium of exchange."
Virtual currencies are unregulated in the United States, but authorities are considering regulation. The Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) has brought U.S.-based cryptocurrency exchanges under its supervision and continues to scrutinize all crypto-related products. Regulation for stablecoins is also in the works.
How Virtual Currencies are Used
Virtual currencies were originally released as payment methods but have not gained widespread use as a medium of exchange in society. However, they are used in some countries by individuals without access to other payment methods or financial services. According to a report by Chainalysis, cryptocurrency adoption is higher in lower middle-income countries.
Types of Virtual Currencies
Virtual currencies can be classified as closed or open based on their operating network.
Closed Virtual Currency
A closed virtual currency operates within a controlled and private ecosystem. It cannot be converted into another virtual or fiat currency. Examples include currencies in gaming systems and airline miles.
Open Virtual Currency
Open virtual currencies, also known as convertible virtual currencies, can be converted to other forms of money. They operate in open ecosystems and can be converted within or outside the platform. Examples include stablecoins and cryptocurrencies.
Advantages of Virtual Currencies
– Virtual currencies can eliminate geographical boundaries.
– Decentralized virtual currencies remove intermediaries during transactions.
– Virtual currencies enable automated transactions through smart contracts.
– Virtual currencies assign value to various objects.
Disadvantages of Virtual Currencies
– Virtual currencies are attractive targets for hackers.
– Virtual currencies can be subject to scams, such as initial coin offerings.
– Unregulated virtual currencies do not offer legal recourses.
– Virtual currencies can experience highly volatile price swings.
Differences Between Digital Currencies, Virtual Currencies, and Cryptocurrencies
– All virtual currencies and cryptocurrencies are digital currencies.
– Digital currencies can be regulated or unregulated.
– Not all digital currencies are secured using cryptography.
In conclusion, virtual currencies are digital representations of value that exist only electronically. Their transactions occur online, and examples include tokens and cryptocurrencies. While virtual currencies offer advantages such as eliminating intermediaries and allowing for automated transactions, they also have disadvantages such as vulnerability to hacking and scams. It is important to understand the differences between virtual currencies, digital currencies, and cryptocurrencies.