Unearned Revenue What It Is How It Is Recorded and Reported
Contents
Unearned Revenue: What It Is, How It Is Recorded and Reported
What Is Unearned Revenue?
Unearned revenue is money received for a service or product that has yet to be provided. It can be thought of as a "prepayment" for goods or services that will be supplied at a later date. The seller has a liability equal to the revenue earned until the good or service is delivered. This liability is noted under current liabilities, as it is expected to be settled within a year.
Unearned revenue is also referred to as deferred revenue and advance payments.
Key Takeaways
- Unearned revenue is money received for a service or product that has yet to be provided.
- It is recorded on a company’s balance sheet as a liability because it represents a debt owed to the customer.
- Once the product or service is delivered, unearned revenue becomes revenue on the income statement.
- Receiving funds early benefits a company as it increases cash flow that can be used for various business functions.
Understanding Unearned Revenue
Unearned revenue is common among companies selling subscription-based products or services that require prepayments. Examples include rent payments made in advance, prepaid insurance, legal retainers, airline tickets, prepayment for newspaper subscriptions, and annual prepayment for software use.
Receiving money before a service is fulfilled is beneficial. Early cash flow can be used for activities like paying interest on debt and purchasing more inventory.
Recording Unearned Revenue
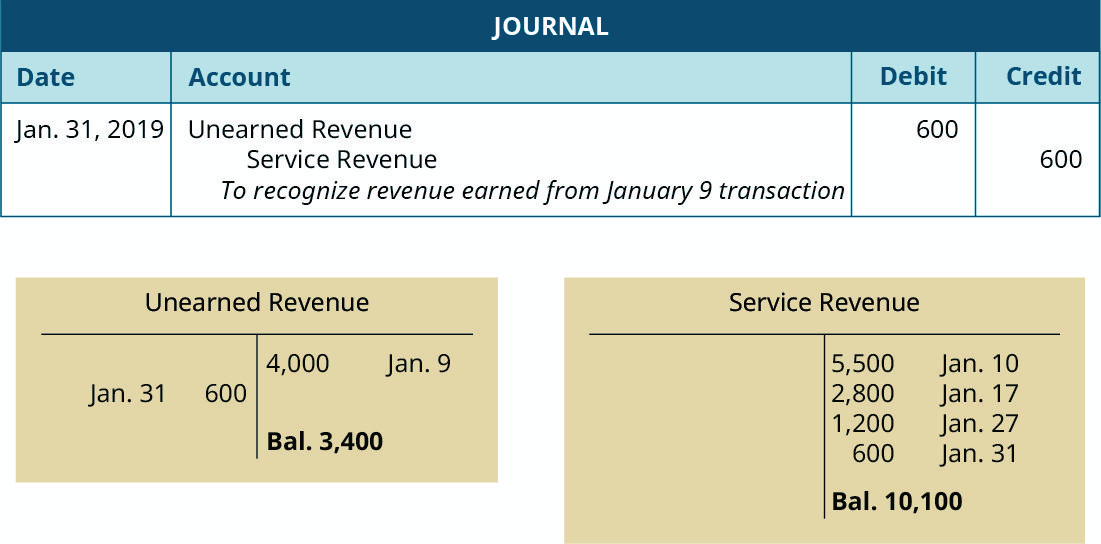
Unearned revenue is recorded on a company’s balance sheet as a liability. It is treated as a liability because the revenue has not yet been earned and represents products or services owed to a customer. As the prepaid service or product is gradually delivered, it is recognized as revenue on the income statement.
If a publishing company accepts $1,200 for a one-year subscription, the amount is recorded as an increase in cash and unearned revenue. Both are balance sheet accounts, so the transaction does not immediately affect the income statement. If it is a monthly publication, the liability or unearned revenue is reduced by $100 ($1,200 divided by 12 months) with each delivery, while revenue is increased by the same amount.
Unearned revenue is usually disclosed as a current liability on a company’s balance sheet. This changes if advance payments are made for goods or services due to be provided 12 months or more after the payment date. In such cases, the unearned revenue will appear as a long-term liability on the balance sheet.
Unearned Revenue Reporting Requirements
The U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) established criteria that a public company must meet to recognize revenue. If these criteria are not met, revenue recognition is deferred.
According to the SEC, there must be collection probability, completed delivery or ownership shifted to the buyer, persuasive evidence of an arrangement, and a determined price.
Example of Unearned Revenue
Morningstar Inc. (MORN) offers products and services for the financial industry, including financial advisors and asset managers. Many of its products are sold through subscriptions. Under this arrangement, subscribers pay upfront and receive the product over time. This creates a situation where the amount is recorded as unearned revenue or deferred revenue.
At the end of the second quarter of 2020, Morningstar had $287 million in unearned revenue, up from $250 million from the prior-year end. The company classifies the revenue as a short-term liability, meaning it expects the amount to be paid over one year for services provided over the same period.
Unearned revenue can provide clues into future revenue, although investors should note the balance change could be due to a change in the business. Morningstar increased quarterly and monthly invoices but is less reliant on up-front payments from annual invoices, meaning the balance has been growing more slowly than in the past.