Transposition Error Definition Causes and Consequences
Contents
Transposition Error: Definition, Causes, and Consequences
Andrew Bloomenthal has over 20 years of editorial experience as a financial journalist and services marketing writer.
What Is a Transposition Error?
A transposition error occurs when a bookkeeper accidentally reverses two adjacent digits while recording transactional data. While this error may seem small, it can have significant financial consequences. Transpositional errors typically occur in accounting firms, brokerages, and other financial services, falling under the broader category of transcription errors.
Key Takeaways
- A transposition error is a data entry mistake where two digits are accidentally reversed.
- These mistakes are caused by human error.
- Though seemingly small, transposition errors can result in significant financial consequences.
- If accounting records show a discrepancy, the difference between the correct and incorrectly-entered amounts will be evenly divisible by 9.
Understanding Transpositional Errors
Transposition errors are generally the result of human error. For example, in accounting, when transferring data from an invoice to a balance sheet, a bookkeeper may incorrectly enter information by mistake. Transposition errors can also occur when checks are filled out incorrectly, resulting in incorrect payment amounts that may cause banking issues like overdrafts. Additionally, transportation errors can result in phone numbers, street addresses, or ZIP codes being incorrectly recorded in customer profiles. While some of these mistakes are easily corrected, transposition errors relating to medicinal dosing information can have tragic consequences in certain cases.
Examples of Transposition Errors
If a company fails to catch and correct transposition errors, the incorrect value of assets may be perpetuated to external agencies and individuals, such as shareholders and the Internal Revenue Service. This can create a chain effect of inaccuracies. For instance, a business may face increased tax liability if the transposition error pushes them into a higher tax bracket. The impact of the error depends on its magnitude. A discrepancy of $0.27, resulting from writing $24.74 instead of $24.47, would have minimal consequences. On the other hand, if $1,823,000 is mistakenly recorded as $1,283,000, the $540,000 error is sure to have a profound financial ripple effect.
Transposition errors made in the trading world are sometimes known as "fat-finger trades." In one famous example, a Japanese trader accidentally placed an order for 1.9 billion shares in Toyota, but the order was luckily canceled.
Identifying Transposition Errors
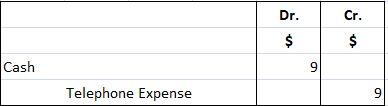
An interesting mathematical phenomenon can expose transposition errors. Specifically, the difference between the incorrectly recorded amount and the correct amount will always be evenly divisible by 9. For example, if a bookkeeper mistakenly writes 72 instead of 27, the resulting 45 error can be evenly divided by 9 to give us 5. Similarly, if a bookkeeper mistakenly records 63 instead of 36, the difference of 27 can be divided by 9 to give us 3. Bank tellers can use this rule to detect errors.
Transposition errors also occur when bookkeepers enter spreadsheet data into the wrong cells.