Market Maker Definition What It Means and How They Make Money
Contents
- 1 Market Maker Definition: What It Means and How They Make Money
- 1.1 What Is a Market Maker?
- 1.2 Understanding Market Makers
- 1.3 How Market Makers Earn Profits
- 1.4 Market Makers vs. Designated Market Makers (DMMs)
- 1.5 Market Makers by Exchange
- 1.6 Example of Market Maker
- 1.7 Who Are Market Makers and What Do They Do?
- 1.8 How Do Market Makers Work?
- 1.9 How Do Market Makers Earn a Profit?
- 1.10 The Bottom Line
Market Maker Definition: What It Means and How They Make Money
Andrew Bloomenthal has over 20 years of editorial experience as a financial journalist and services marketing writer.
What Is a Market Maker?
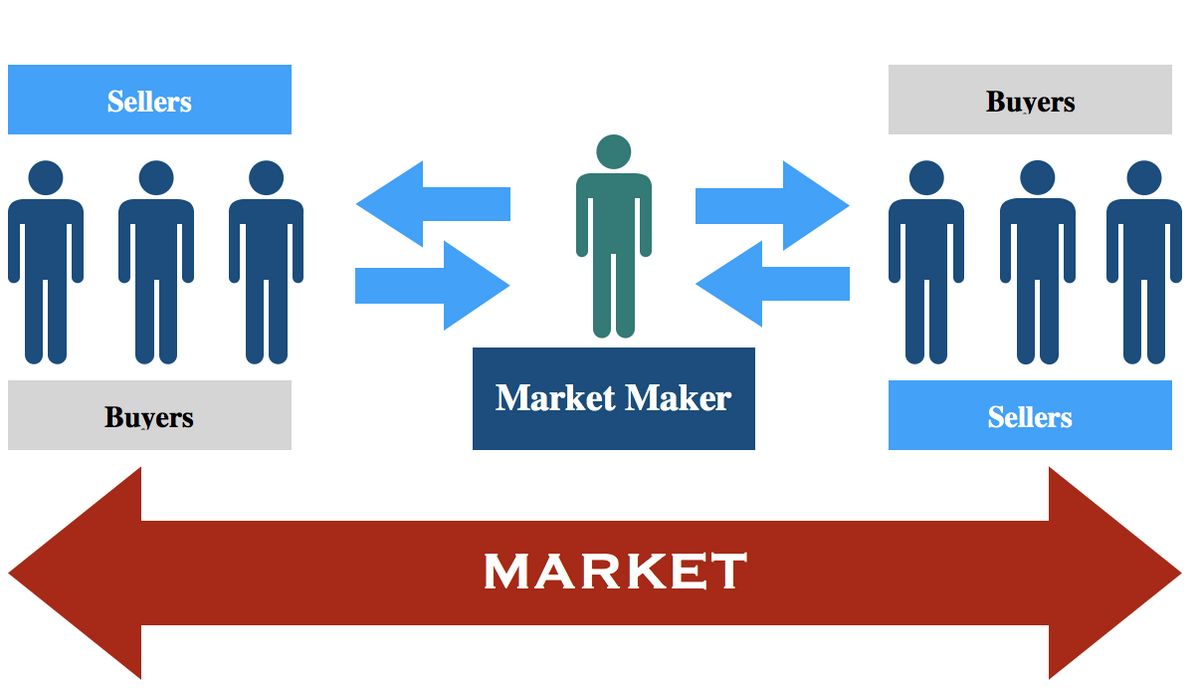
The term market maker refers to a firm or individual who actively quotes two-sided markets in a particular security by providing bids and offers (asks) along with the market size. Market makers provide liquidity and profit from the bid-ask spread. They may also make principal trades.
Key Takeaways
- A market maker is an individual participant or member firm of an exchange that buys and sells securities for its own account.
- Market makers provide liquidity and profit from the bid-ask spread.
- Brokerage houses are the most common types of market makers, providing solutions for investors.
- Market makers are compensated for the risk of holding assets because a security’s value may decline between its purchase and sale to another buyer.
- While brokers compete against one another, specialists post bids and asks and ensure accurate reporting.
Understanding Market Makers
Many market makers are brokerage houses that provide trading services for investors to keep financial markets liquid. Market makers can also be individual traders, commonly known as locals. Most market makers work for large institutions to facilitate high-volume purchases and sales.
Each market maker displays buy and sell quotations for a guaranteed number of shares. Once a market maker receives an order from a buyer, they immediately sell their position of shares from their inventory to complete the order.
Market makers must continuously quote prices at which they will buy and sell securities and specify the volume and frequency they are willing to trade. They must adhere to these parameters in all market outlooks. When markets become volatile, market makers must remain disciplined to ensure smooth transactions.
Making a market signals a willingness to buy and sell securities to broker-dealer firms that are members of the exchange.
How Market Makers Earn Profits
Market makers are compensated for the risk of holding assets because they may see a decline in the value of a security after it has been purchased and before it’s sold. Consequently, they commonly charge a spread on each security they cover. High-volume trading allows market makers to earn daily profits from small spreads.
Market makers must operate under an exchange’s bylaws approved by a country’s securities regulator, such as the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC). Rights and responsibilities of market makers vary by exchange and financial instrument, such as equities or options.
Market Makers vs. Designated Market Makers (DMMs)
Many exchanges use a system of market makers who compete to set the best bid or offer to win incoming orders. However, some entities, like the New York Stock Exchange (NYSE), have a designated market maker (DMM) system instead.
DMMs are lone market makers with a monopoly over the order flow in a particular security. Bids and asks are competively forwarded by investors in an auction market like the NYSE.
The specialist posts these bids and asks for the market to see, ensures accurate reporting, maintains the best price, executes marketable trades, and maintains order on the floor.
The specialist sets the opening price for the stock each morning based on supply and demand.
$40.72 trillion
Total market capitalization of domestic companies listed in the United States.
Market Makers by Exchange
Market makers provide trading services for investors in the securities market, boosting liquidity. They operate and compete within securities exchanges. Some popular market makers include:
NYSE and Nasdaq
The NYSE and Nasdaq are the two main stock exchanges in the United States. Some market makers in New York include:
- Credit Suisse
- Deutsche Bank
- Goldman Sachs
- KCG Americas
- Timber Hill
Frankfurt Stock Exchange (FRA)
The Frankfurt Stock Exchange (FRA) is one of seven stock exchanges in Germany. Market makers on Xetra include:
- Berenberg
- JPMorgan
- Morgan Stanley
- Optiver
- UBS Europe
London Stock Exchange Group
The London Stock Exchange (LSE) is part of the London Stock Exchange Group. Market makers in London include:
- BNP Paribas
- GMP Securities Europe
- Liberium Capital
- Mediobanca
- Standard Chartered
Tokyo Exchange Group
The Tokyo Exchange Group provides reliable venues for trading listed securities and derivatives instruments. Market makers in Tokyo include:
- ABN AMRO Clearing
- Nissan Securities
- Nomura Securities
- Phillip Securities
- Societe Generale
Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX)
The Toronto Stock Exchange (TSX) is Canada’s largest exchange. Market makers on the TSX include:
- BMO Nesbitt Burns
- Integral Wealth Solutions
- Questrade
- Scotia Capital
- TD Securities
Market-making facilitates smoother financial markets and promotes transactions and investment activities.
Example of Market Maker
For example, a market maker in XYZ stock may provide a quote of $10.00 – $10.05 or 100×500. This means they bid (buy) $10.00 for 100 shares and offer (sell) 500 shares at $10.05. Other market participants can buy from the market maker at $10.05 or sell to them at $10.00.
Who Are Market Makers and What Do They Do?
Market makers participate in the securities market by providing trading services, bids, and offers to boost liquidity. They typically work for brokerage houses and profit from the bid-ask spread.
How Do Market Makers Work?
Market makers compete with each other within securities exchanges by setting competitive bid and ask offers. Some exchanges use a specialist system with a sole market maker who makes bids and asks visible to the market. Specialists ensure fair and timely executions of marketable trades.
How Do Market Makers Earn a Profit?
Market makers earn a profit from the spread between bid and offer prices. They are compensated for holding assets that may decrease in price between purchase and sale. For example, if Apple stock has a bid price of $50 and an ask price of $50.10, the market maker bought it for $50 and is selling it for $50.10, earning a profit of $0.10.
The Bottom Line
The market consists of entities such as corporations, exchanges, traders, investors, and market makers. Market makers provide bids and offers and inject liquidity into the markets, facilitating smoother transactions and investment activities.