Mandatory Convertible What it is How it Works
Contents
Mandatory Convertible: What It Is and How It Works
What Is a Mandatory Convertible?
A mandatory convertible is a type of bond that must be converted into common stock by a specific date. Unlike traditional convertible bonds, which offer the option to convert, mandatory convertibles require conversion.
Key Takeaways
- A mandatory convertible is a bond that must be converted into common stock by a specific date.
- Mandatory convertibles provide higher yields than regular convertible bonds.
Mandatory Convertibles Explained
A mandatory convertible is a security that automatically converts to common equity on or before a predetermined date. This hybrid security guarantees a certain return until the conversion date, after which a higher return is possible. In contrast, a regular convertible bond gives the holder the option to convert the fixed income security into shares. The investor may choose to convert or keep the bonds in their portfolio depending on market conditions, providing downside protection if the company’s share price underperforms.
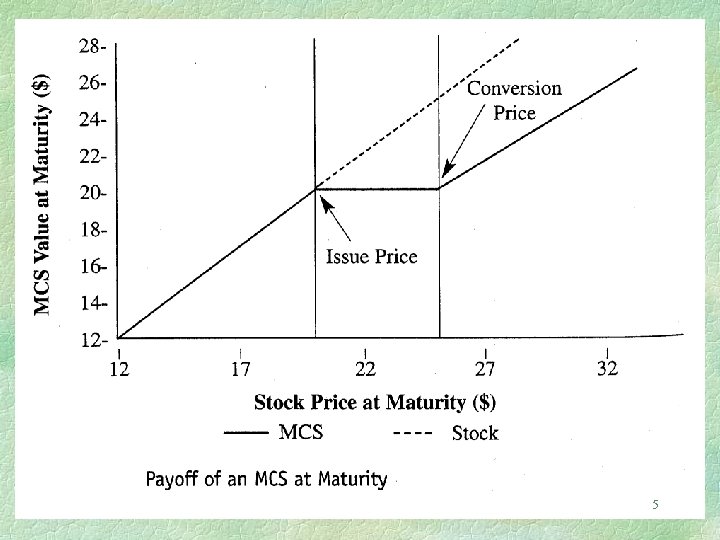
Mandatory convertibles offer higher yields compared to ordinary convertibles to compensate for the lack of conversion options. The issue price of a mandatory convertible is equal to the price of the common stock. The trust indenture specifies the conversion price, which is the price at which the debt securities can be converted into common stock at a premium to the issue price upon maturity. Typically, there are two conversion prices for a mandatory convertible. The first sets a price where the investor would receive the equivalent of the bond’s par value in shares, while the second determines a price where the investor would earn more than par. The conversion ratio may also be stipulated instead of the conversion price, indicating the number of shares each bond can convert into. This ratio changes based on the company’s stock price.
Mandatory convertibles have a similar application to mandatory convertible preferred shares, whereby preferred shareholders must convert their shares to common stock on a specified date.
Other Considerations
Companies can raise capital through equity or debt issuance. Equity issuance involves dividends to shareholders, while debt issuance requires periodic interest payments to bondholders. The choice between equity and debt depends on the company’s cost of each security issuance.
Sometimes, companies deviate from pure equity or debt issues to adjust their capital structure or reduce their cost of capital. When market conditions are unfavorable for an equity issue or the issuance would impact the share price negatively, a company may opt for debt with a mandatory convertible feature. This allows the debt to be converted into equity at a more opportune time. The trust indenture will highlight if the bond has a mandatory convertible feature at the time of issuance.