Funded Debt Overview and Types in Corpporate Accounting

Funded Debt: Overview and Types in Corporate Accounting
What Is Funded Debt?
Funded debt in corporate accounting is a company’s debt that matures in more than one year or one business cycle. This type of debt is funded by interest payments made over the term of the loan.
Funded debt is also known as long-term debt since the term exceeds 12 months. It is different from equity financing, where companies sell stock to raise capital.
Key Takeaways:
– Funded debt is a company’s debt that matures in more than one year or one business cycle.
– Funded debt is also called long-term debt and consists of long-term, fixed-maturity borrowings.
– Examples of funded debt include bonds with maturity dates of more than a year, convertible bonds, long-term notes payable, and debentures.
Understanding Funded Debts
When a company takes out a loan, it does so by issuing debt or securing financing with a lending institution. Loans are taken out to finance long-term capital projects, such as adding a new product line or expanding operations. Funded debt refers to any financial obligation that extends beyond a 12-month period or the current business year or operating cycle. It is the term for the portion of a company’s long-term debt made up of fixed-maturity borrowings.
Funded debt is an interest-bearing security recognized on a company’s balance sheet. A funded debt usually includes interest payments that serve as income to lenders. From an investor’s perspective, a higher percentage of funded debt to total debt disclosed in the debt note indicates better financial health.
Funded debt is generally a safe way of raising capital for the borrower due to its long-term nature. The interest rate can be locked in for a longer period, providing stability.
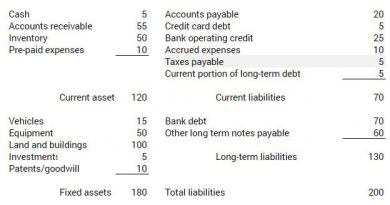
Examples of funded debt include bonds with maturity dates of more than a year, convertible bonds, long-term notes payable, and debentures. Funded debt is sometimes calculated as long-term liabilities minus shareholders’ equity.
Funded vs. Unfunded Debt
Corporate debt can be categorized as funded or unfunded. Funded debt is long-term borrowing, while unfunded debt is a short-term financial obligation due within a year. Short-term liabilities are often used by companies with cash-flow issues.
Examples of short-term liabilities include corporate bonds maturing in one year and short-term bank loans. Short-term financing offers flexibility but exposes the firm to higher interest rate and refinancing risks.
Analyzing Funded Debt
Analysts and investors use the capitalization ratio (cap ratio) to compare a company’s funded debt to its capitalization or capital structure. The cap ratio is calculated by dividing long-term debt by total capitalization (long-term debt + shareholders’ equity). A high capitalization ratio indicates higher insolvency risk, but it can also have tax advantages. The cap ratio depends on the industry, business line, and business cycle.
Another ratio that incorporates funded debt is the funded debt to net working capital ratio. It helps determine if long-term debts are in proportion to capital. An ideal ratio is less than one, where long-term debts should not exceed net working capital. However, the ideal ratio may vary across industries.
Debt Funding vs. Equity Funding
Companies have options to raise capital, such as debt financing and equity financing. In equity financing, companies sell stock to investors on the open market, allowing investors to own a stake in the company. Equity financing shares profits and may require relinquishing control to shareholders.
Debt financing has advantages over equity financing. It allows companies to retain full ownership as there are no shareholders claiming equity stakes. The interest paid on debt financing is generally tax-deductible, reducing the tax burden.