What Are Stock Options Parameters and Trading With Examples
Contents
- 1 Stock Options: Parameters and Trading, Examples
- 1.1 What Is a Stock Option?
- 1.2 Understanding Stock Options
- 1.3 Stock Option Parameters
- 1.4 Trading Stock Options
- 1.5 Example of Stock Options
- 1.6 Employee Stock Options
- 1.7 Calculating the Value of Stock Options
- 1.8 Exercising Stock Options
- 1.9 Stock Options and Taxes
- 1.10 Types of Stock Option Plans
- 1.11 Why Buy an Option?
- 1.12 Main Types of Stock Options
- 1.13 How Stock Options Work
- 1.14 Exercising a Stock Option
- 1.15 The Bottom Line
Stock Options: Parameters and Trading, Examples
What Is a Stock Option?
A stock option, also known as an equity option, gives an investor the right to buy or sell a stock at an agreed-upon price and date. There are two types of options: puts, which bet on a stock falling, and calls, which bet on a stock rising.
Stock options are a form of equity derivative that use shares of stock or a stock index as their underlying asset.
Employee stock options (ESOs) are a type of equity compensation given by companies to some employees or executives. They are different from listed equity options traded on the market, as they are restricted to a particular corporation issuing them to their own employees.
Key Takeaways
- Stock options give a trader the right to buy or sell shares at an agreed-upon price and date.
- Stock options are a common form of equity derivative.
- One options contract represents 100 shares of the underlying stock.
- There are two primary types of options contracts: calls and puts.
- ESOs are call options granted to certain employees as compensation.
Understanding Stock Options
Options are a type of financial instrument known as a derivative. They derive their worth from the value of an underlying security or asset. Stock options derive their worth from shares of a company’s stock.
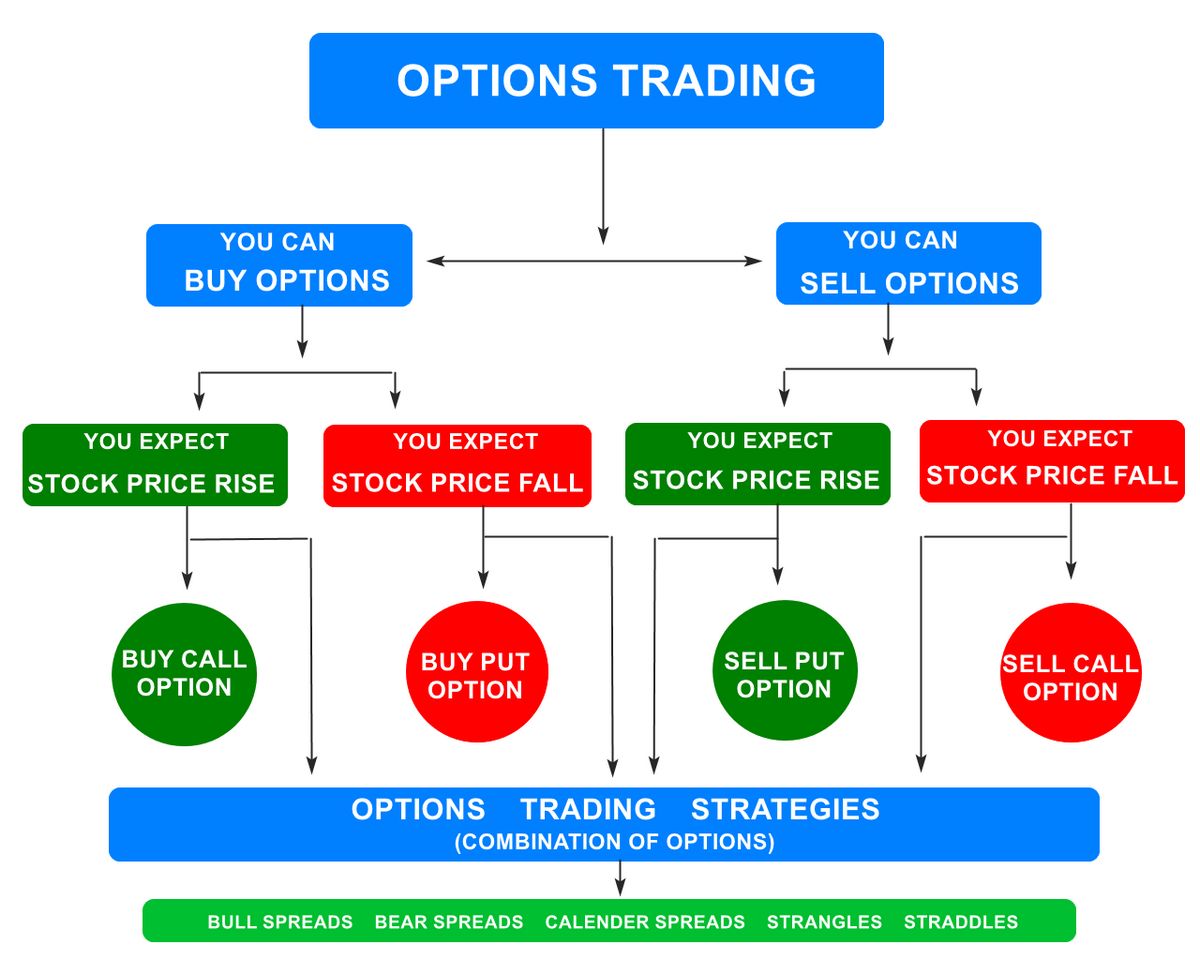
There are two basic types of stock options:
- Call options give the holder the right to buy the asset at a stated price within a specific timeframe.
- Put options give the holder the right to sell the asset at a stated price within a specific timeframe.
For options to be profitable, they must be "in the money," meaning the stock price must be above the call option strike price or below the put option strike price. Otherwise, they are "out of the money" and contain only time value.
Equity options allow investors and traders to take long or short positions in a stock without actually buying or shorting the stock. This is advantageous because it requires less capital and offers more leverage. Traders can profit from price movements in the underlying stock.
Exercising an option means using the right to convert the contract into shares at the strike price.
Stock Option Parameters
American vs. European Styles
American options can be exercised at any time between purchase and expiration, while European options can only be exercised on the expiration date.
Expiration Date
Options contracts exist for a certain period of time, known as the expiration date. Options with longer expiration dates have more time value and greater chances of being in-the-money. Expiration dates follow a fixed schedule, ranging from daily and weekly to monthly and yearly.
Strike Price
The strike price is the price at which an option should be exercised. It represents the level at which the trader expects the stock to be above or below by the expiration date.
Contract Size
Contracts represent a specific number of underlying shares. One contract is equal to 100 shares of the underlying stock.
Premium
The premium is the price paid for an option. It is determined by multiplying the price of the call or put by the number of contracts bought, then multiplying that by 100.
The volatility of the underlying security affects options pricing. Higher volatility leads to higher premiums.
Trading Stock Options
Stock options are listed for trading on various exchanges, such as the Chicago Board Options Exchange (CBOE) and the International Securities Exchange (ISE).
Options can be bought or sold based on the trader’s strategy. If a trader believes a stock will rise, they can buy a call option or sell a put option. If they believe a stock will fall, they can sell a call option or buy a put option. Selling options generates premium income.
Investors can also use option spreads to minimize risk and capitalize on premium extraction.
Example of Stock Options
In this example, a trader believes Nvidia Corp’s stock will rise to over $170. They buy 10 January $170 calls for $16.10 per contract, resulting in a total cost of $16,100. If the stock rises above $170 by expiration, the trader earns a profit. Otherwise, the options expire worthless.
If the trader believes Nvidia will fall, they can buy 10 January $120 puts for $11.70 per contract, costing $11,700. For the trader to profit, the stock must fall below $108.30. Otherwise, the options expire worthless.
Employee Stock Options
Employee stock options (ESOs) are a type of equity compensation granted by companies to their employees and executives. ESOs give employees the right to buy the company’s stock at a specified price for a certain period of time.
ESOs often have vesting schedules that limit the ability to exercise. If the stock price rises once the vesting periods end, employees can profit by exercising their options.
ESOs usually come with a "cliff" period during which the employee must work with the company to receive their shares. After the cliff, options continue to vest on schedule, even if the employee leaves the company.
ESOs are not publicly-traded and have a dilutive effect on the company as they increase the number of shares outstanding.
Calculating the Value of Stock Options
If the company is publicly traded, the value of stock options depends on the current value of the stock. Calculate the value by comparing the option price and the current market price for the same number of shares.
If the company is not publicly traded, determining the value of stock options becomes more speculative. It may be based on a valuation of the company or other factors.
The number of shares or options available also affects their value. More shares/options can lower the value of each individual share/option.
The value of stock options also depends on the stock’s price movement. If the stock price is above the strike price, the options have value.
Exercising Stock Options
Exercising stock options involves buying (for calls) or selling (for puts) the underlying stock at the strike price. This is typically done before expiration if the option is in the money or at expiration if any amount in the money. Exercising the option eliminates it, and the trader can choose to close the position or hold the shares.
If the cash is not available, there are ways to exercise stock options without upfront payment, such as exercise-and-sell or exercise-and-sell-to-cover strategies.
Stock Options and Taxes
Stock option exercises are subject to taxes based on the type of options and the timing of exercise and sale.
Taxes for Statutory Stock Options
Statutory stock options granted through an employee stock purchase plan or an incentive stock option (ISO) are not taxed when granted. Taxes are paid when the option is exercised, based on the bargain element (the difference between the market value and the exercise price). Capital gains tax is also applied when the shares are sold.
Taxes for Nonstatutory Stock Options
Nonstatutory stock options not granted through an employee stock purchase plan or ISO are taxed differently. Taxable income depends on whether the fair market value of the option can be readily determined. If it can, the option is treated as taxable income at the time it is granted. Otherwise, it is taxed as capital gains when the option is exercised or transferred.
Types of Stock Option Plans
Stock option plans can be structured in different ways, providing varying levels of risk and incentives to both employers and employees.
| Employees receive options worth a fixed value annually | Employees receive a fixed number of options annually | Employees receive a single, large grant of options |
| Keeps compensation in line with competitors | Links pay and performance strongly | Attracts top employees with high compensation |
| Minimizes risk of employees leaving for better compensation | Incentivizes company growth and stock value increase | Risky for companies prone to market volatility |
| Offers minimal incentive to employees | Results in lower pay during market turmoil | Decrease in value can remove incentive to boost stock or stay at the company |
Why Buy an Option?
Stock options allow investors to bet on the rise or fall of a stock by a specific date. Large corporations often purchase stock options to hedge risk exposure. Options also allow investors to speculate on stock prices, though this carries higher risk.
Main Types of Stock Options
Investors can choose between call options and put options when trading stock options. Call options bet on a stock rising, while put options bet on a stock falling. Options are purchased as contracts representing 100 shares of the underlying stock.
How Stock Options Work
Investors speculate on a stock’s future price movement through options. For example, buying a call option allows the investor to profit if the stock price rises above the strike price. Exercising the option involves converting it into shares at the strike price.
Exercising a Stock Option
Exercising a stock option involves buying (for calls) or selling (for puts) the underlying stock at the strike price. Options are typically exercised before expiration if they are in the money, resulting in the delivery of the underlying asset.
The Bottom Line
Stock options are derivatives that give the holder the right to buy or sell shares at a specified price and date. They are a common form of equity derivative. ESOs are a type of equity compensation granted by companies to their employees. Options pricing is influenced by volatility, and exercising options can generate profits for traders.



