Trade-Weighted Dollar What It Is and How It Works
Trade-Weighted Dollar: What It Is and How It Works
What Is the Trade-Weighted Dollar?
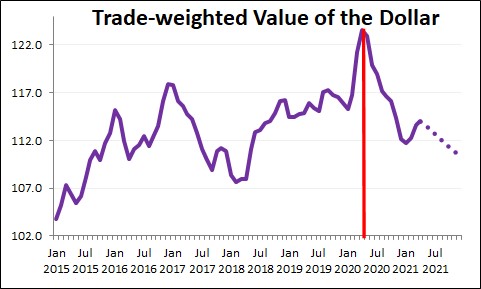
The trade-weighted dollar is an index created by the Federal Reserve (Fed) to measure the value of the U.S. dollar (USD) versus trading partners.
Key Takeaways:
– The trade-weighted dollar is an index created by the Fed to measure the value of the USD.
– The dollar is measured based on its competitiveness versus trading partners.
– The index gives importance to currencies most widely used in international trade.
– It is used to determine the U.S. dollar’s purchasing value.
– It summarizes the effects of dollar appreciation and depreciation against foreign currencies.
How the Trade-Weighted Dollar Is Used:
The trade-weighted dollar determines the U.S. dollar’s purchasing value and summarizes the effects of dollar appreciation and depreciation against foreign currencies. When the value of the dollar increases, imports to the U.S. become less expensive and exports to other countries become more expensive.
The trade-weighted dollar is a measurement of the foreign exchange value of the U.S. dollar compared to certain foreign currencies. It gives importance and weight to currencies most widely used in international trade. Changes in each currency have a unique effect on the trade-weighted dollar and corresponding indexes.
History of the Trade-Weighted Dollar:
The Trade-Weighted Dollar Index, also known as the Broad Index, was introduced in 1998 in response to the implementation of the euro. It was intended to reflect current U.S. trade patterns more accurately.
The Fed selected 26 currencies to use in the index, anticipating the adoption of the euro by eleven countries of the European Union (EU). These 26 economies accounted for about 90% of total bilateral trade with the U.S.
Trade-Weighted Dollar Index vs. U.S. Dollar Index:
The primary index used to measure the strength of the USD is the U.S. Dollar Index (USDX). Created in 1973, it is composed of a basket of six currencies: the euro (EUR), Japanese yen (JPY), British pound (GBP), Canadian dollar (CAD), Swedish krona (SEK), and Swiss franc (CHF).
The Fed introduced the Trade-Weighted Dollar Index as an alternative to the USDX. It includes more currencies and periodically reviews the index’s composition. The Trade-Weighted Dollar Index includes countries from all over the world, and its weighting is updated once a year based on annual trade data published by the Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA).
What Is an Index?
An index is a benchmark measurement that gauges one investment’s performance against another. It is an invaluable tool for investors.
What Is Foreign Exchange?
Foreign exchange is the process of converting one country’s currency to that of another country using a specified rate. The rates move up and down regularly as influenced by supply and demand, making diligent tracking important for investors.
What Countries Make Up the European Union?
The European Union includes 27 countries as of 2024, located in Europe. Belgium, Italy, France, Germany, Denmark, Ireland, Sweden, and Finland are among them. The United Kingdom left the EU in 2020, and the Ukraine’s membership application is still pending.
The Bottom Line:
The trade-weighted dollar, also known as the Broad Index, was introduced in 1998 to accurately reflect current U.S. trade patterns. It measures the value of the U.S. dollar compared to the currencies of other nations, focusing on those most commonly used in international trade. It gauges appreciation and depreciation and is valuable for currency traders.