What Are Preference Shares and What Are the Types of Preferred Stock
Contents
Preference shares, also known as preferred stock, are shares of a company’s stock with dividends paid to shareholders before common stock dividends. In case of bankruptcy, preferred stockholders are paid before common stockholders.
Most preference shares have a fixed dividend, while common stocks usually do not. Preferred stock shareholders typically have no voting rights, unlike common shareholders.
Key Takeaways
- Preference shares (preferred stock) are company stock with dividends paid to shareholders before common stock dividends.
- There are four types of preferred stock – cumulative (guaranteed), non-cumulative, participating, and convertible.
- Preference shares are ideal for risk-averse investors and are callable (the issuer can redeem them at any time).
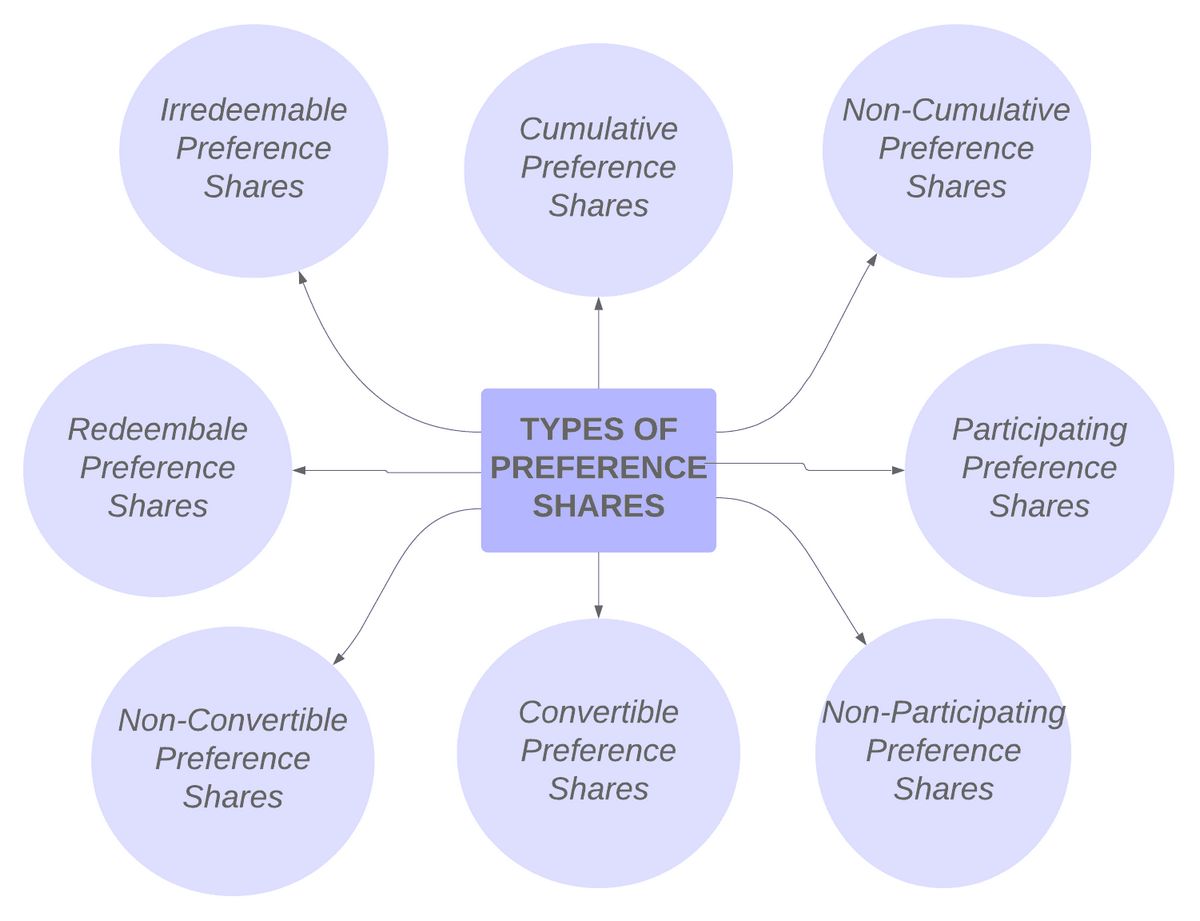
Preference shares fall into four categories: cumulative preferred stock, non-cumulative preferred stock, participating preferred stock, and convertible preferred stock.
Cumulative preferred stock requires the company to pay shareholders all dividends, even those omitted in the past, before common shareholders receive their dividends. Unpaid dividends are known as "dividends in arrears" and must be paid to the current stock owner. Sometimes, additional compensation (interest) is awarded to the holder of this type of preferred stock.
Quarterly Dividend = [(Dividend Rate) x (Par Value)] ÷ 4
Cumulative Dividends per share = Quarterly Dividend x Number of Missed Payments
Non-cumulative preferred stock does not issue omitted or unpaid dividends. Shareholders of non-cumulative preferred stock have no right or power to claim foregone dividends in the future.
Participating preferred stock provides shareholders with preferred dividends plus an additional dividend if common shareholders receive dividends above a specific per-share amount. In case of liquidation, participating preferred shareholders may be paid back the stock’s purchasing price and a share of remaining proceeds.
Convertible preferred stock includes an option for shareholders to convert their preferred shares into common shares after a pre-established date. Conversion usually happens at the shareholder’s request, but the company may have a provision to force the conversion. The value of convertible common stocks depends on the performance of the common stock.
Preference shares, or preferred shares, are a type of security similar to common shares and fixed-income securities. Preference shareholders have priority in receiving company dividends but often lack voting rights or upside participation.
The four main types of preference shares are cumulative preferred, non-cumulative preferred, participating preferred, and convertible. Cumulative preferred shares entitle holders to retroactive dividends, while non-cumulative preferred shares do not. Cumulative preferred shares are generally more expensive. Participating preferred shares offer additional dividends based on performance targets. Convertible preferred shares can be converted into common shares.
In bankruptcy, different securityholders have claims to a company’s assets. The order in which they receive their share depends on their security agreements. Preference shares have priority over common shares but lower priority than corporate bonds or other fixed-income securities.