What Is a Bid-Ask Spread and How Does It Work in Trading
Contents
- 1 What Is a Bid-Ask Spread and How Does It Work in Trading?
- 1.1 What Is a Bid-Ask Spread?
- 1.2 Understanding Bid-Ask Spreads
- 1.3 The Bid-Ask Spread’s Relation to Liquidity
- 1.4 Bid-Ask Spread Example
- 1.5 Elements of the Bid-Ask Spread
- 1.6 How Does Bid-Ask Spread Work?
- 1.7 What Causes a High Bid-Ask Spread?
- 1.8 What Is an Example of a Bid-Ask Spread in Stocks?
- 1.9 The Bottom Line
What Is a Bid-Ask Spread and How Does It Work in Trading?
Cierra Murry is an experienced banking consultant, loan signing agent, and arbitrator with over 15 years of expertise in financial analysis, underwriting, loan documentation, loan review, banking compliance, and credit risk management.
What Is a Bid-Ask Spread?
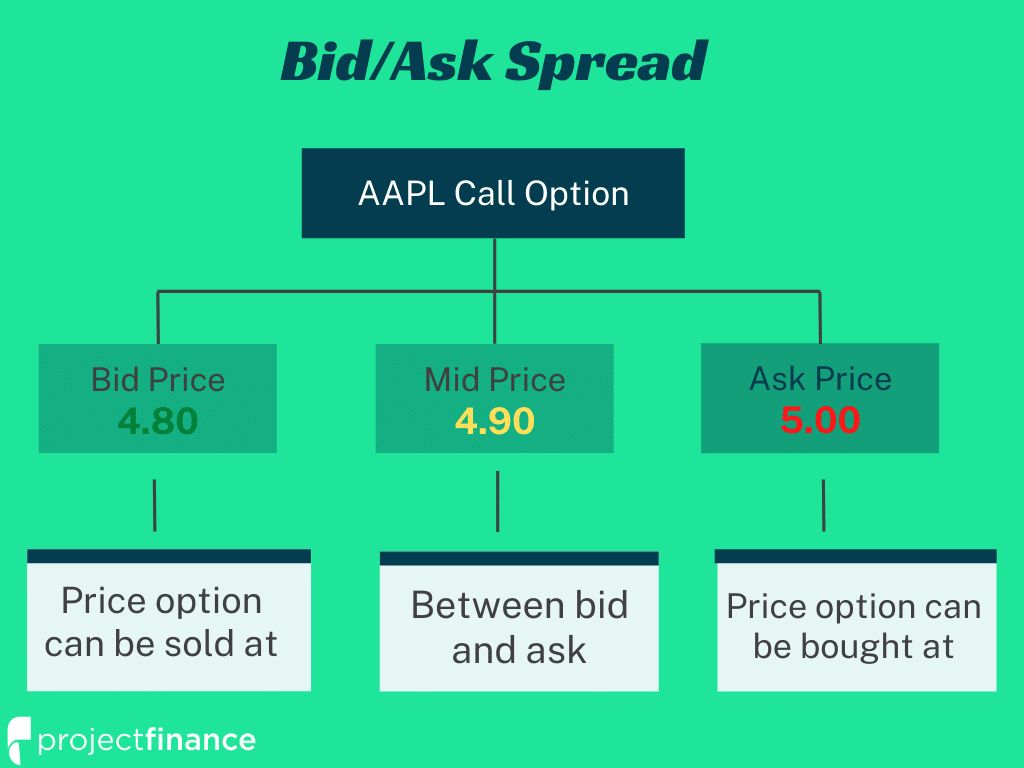
A bid-ask spread is the difference between the ask price and the bid price for an asset in the market. It represents the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept.
Sellers receive the bid price while buyers pay the ask price.
Key Takeaways
- A bid-ask spread is the difference between the highest price a buyer is willing to pay and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept.
- The spread is the transaction cost. Price takers buy at the ask price and sell at the bid price, while market makers buy at the bid price and sell at the ask price.
- The bid represents demand, and the ask represents supply for an asset.
- The bid-ask spread is a measure of market liquidity.
Understanding Bid-Ask Spreads
A security’s price is the market’s perception of its value at any given point in time. To understand the "bid" and "ask," we must consider the price taker (trader) and the market maker (counterparty).
Market makers, often employed by brokerages, offer to sell securities at the ask price and bid to purchase securities at the bid price. When an investor initiates a trade, they accept one of these two prices based on their intention to buy (ask price) or sell (bid price) the security.
The spread, the difference between the two prices, is the primary transaction cost outside of commissions. Market makers collect this spread through the natural flow of processing orders at the bid and ask prices. This is what financial brokerages refer to as revenue derived from traders "crossing the spread."
The bid-ask spread reflects the supply and demand for an asset. When these two prices move apart, it indicates a change in supply and demand.
The depth of the bids and asks greatly impacts the bid-ask spread. If fewer participants place limit orders to buy or sell a security, the spread may widen significantly. It’s crucial to consider the bid-ask spread when placing a buy-limit order to ensure successful execution.
Market makers and professional traders may widen the difference between the best bid and ask prices in response to perceived risks in the markets. This can lead to larger than usual bid-ask spreads.
The Bid-Ask Spread’s Relation to Liquidity
The bid-ask spread varies among assets primarily due to differences in liquidity. The bid-ask spread serves as a measure of market liquidity. More liquid assets have lower spreads, while less liquid assets, like small-cap stocks, may have spreads equivalent to 1% to 2% of the asset’s lowest ask price.
The bid-ask spread may also reflect the market maker’s perceived risk in offering a trade. Options or futures contracts, for instance, may have larger bid-ask spreads compared to forex or equities trades. The spread width may also depend on the speed at which prices could change.
Bid-Ask Spread Example
If the bid price for a stock is $19 and the ask price for the same stock is $20, the bid-ask spread for that stock is $1. The bid-ask spread can also be expressed as a percentage of the lowest ask price.
In the example above, the bid-ask spread in percentage terms would be calculated as $1 divided by $20 (the bid-ask spread divided by the lowest ask price) to yield a bid-ask spread of 5% ($1 / $20 x 100). This spread would close if a potential buyer offered to purchase the stock at a higher price or if a potential seller offered to sell the stock at a lower price.
Elements of the Bid-Ask Spread
Bid-ask spread trades can be conducted in various types of securities, foreign exchange, and commodities.
Traders utilize the bid-ask spread as an indicator of market liquidity. High friction between supply and demand creates a wider spread.
Most traders prefer to use limit orders instead of market orders, as this allows them to choose their entry points rather than accepting the current market price. However, using the bid-ask spread incurs a cost as two simultaneous trades are being conducted.
How Does Bid-Ask Spread Work?
A bid-ask spread in financial markets represents the difference between the asking price and the bidding price of a security or asset. It is the highest price a buyer is willing to offer (bid price) and the lowest price a seller is willing to accept (ask price). Assets with narrow bid-ask spreads typically have high demand, while those with wide spreads may experience low demand and larger price discrepancies.
What Causes a High Bid-Ask Spread?
Bid-ask spreads, also known as "spreads," can be high due to several factors. Liquidity plays a primary role, with heavily traded stocks having smaller spreads (e.g., Google, Apple, Microsoft).
On the other hand, unknown or unpopular securities on a given day, such as small-cap stocks with lower trading volumes and lower investor demand, may have higher bid-ask spreads.
What Is an Example of a Bid-Ask Spread in Stocks?
Consider a trader looking to purchase 100 shares of Apple at $50. The current market offers 100 shares at $50.05. In this case, the spread would be $0.05 ($50.00 – $50.05), which may seem small for one trade. However, on large trades, this spread can make a significant difference. Narrow spreads are generally more favorable. For this example, the total value of the bid-ask spread would be $5 (100 shares x $0.05).
The Bottom Line
The bid-ask spread is an effective measure of liquidity, as more liquid securities tend to have smaller spreads, while illiquid ones have larger spreads. Investors should monitor the spread of any security they wish to trade to understand its frequency of trading and determine the appropriate order type for their transactions.



