What Are Consensus Mechanisms in Blockchain and Cryptocurrency
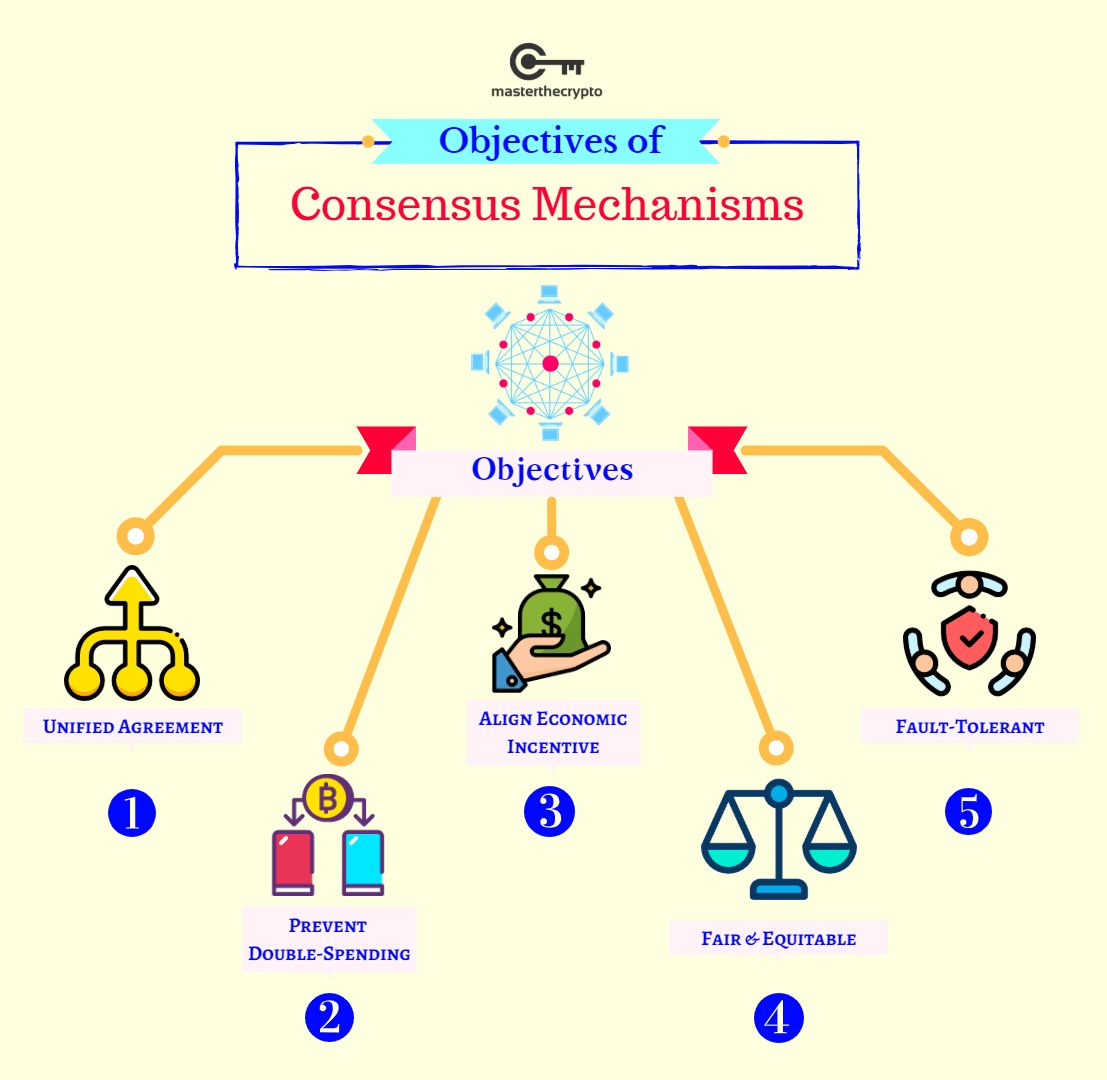
A consensus mechanism is a program used in blockchain systems to achieve distributed agreement about the ledger’s state. It is implemented in a network with many processes and users. Cryptocurrencies, blockchains, and distributed ledgers benefit from their use because the consensus mechanism replaces human verifiers and auditing.
The Bitcoin blockchain uses Proof-of-Work (PoW), which requires computational power to solve an encrypted puzzle, called the hash. After the hash is solved by one miner (or a group), Bitcoin’s PoW requires every node on the network to verify the changed data. This verification checks the data structure, block header hash, block timestamp, block size, and the first transaction. It then completes a long transaction verification checklist, which is much faster than mining and human verification.
Key Takeaways:
– A consensus mechanism achieves agreement, trust, and security across a decentralized network.
– Proof-of-Work (PoW) and Proof-of-Stake (PoS) are prevalent consensus mechanisms.
– Consensus mechanisms secure information through encryption and automated group verification.
In the 1980s and 90s, shared databases were created for multiple users to access information. Centralized networks with administrators evolved, granting user rights and maintaining data integrity.
These shared databases became distributed ledgers, recording information for users in different locations. Preventing data tampering and unauthorized access became a significant issue. To automate distributed database management, distributed autonomous consensus was created. Programs on a network agreed on a database’s state using cryptographic techniques. Hashes were created to ensure data validity.
Consensus mechanisms were developed, credited to Satoshi Nakamoto. However, many other researchers contributed to their development.
There are different consensus mechanism algorithms, each working on different principles.
Proof of Work (PoW) is used by popular cryptocurrency networks like Bitcoin and Litecoin. It requires participants to prove their work to add new transactions to the blockchain, but it consumes high energy and processing time.
Proof of Stake (PoS) is a low-cost, low-energy alternative to PoW. It allocates responsibility based on the virtual currency tokens held, but it can incentivize hoarding.
Proof of History (PoH) and Proof of Elapsed Time (PoET) use cryptographic encoding to achieve consensus without extensive resource consumption.
Other consensus algorithms include Proof of Capacity (PoC), which shares memory space on the blockchain network, and Proof of Activity (PoA), a hybrid of PoW and PoS. Proof of Burn (PoB) requires transactors to send small amounts of cryptocurrency to inaccessible wallets, effectively removing them from existence.
Consensus mechanisms are essential in distributed ledger networks for enterprises. Different mechanisms, like proof-of-work, can be chosen based on their level of consensus.
The future of cryptocurrency remains uncertain, but consensus mechanisms will continue to play a vital role in data safety and integrity.
The best consensus mechanism depends on user needs. Proof of work is best for Bitcoin, while proof of stake is favored by the Ethereum community. Other mechanisms may be better for enterprises, businesses, or personal use.
Proof of stake is one example of a consensus mechanism. Users stake their tokens to conduct work on the blockchain.
Several types of consensus mechanisms have been created but few implemented. Examples include delegated proof of stake, proof of importance, proof of elapsed time, proof of authority, and proof of capacity. These mechanisms validate data changes using different concepts.
Consensus mechanisms are essential for distributed ledgers, databases, and blockchains. They verify data inputs and outputs, automatically auditing digital transactions without human oversight. They create an environment of unalterable and secure information.