What Are Administrative Expenses and What Are Some Examples
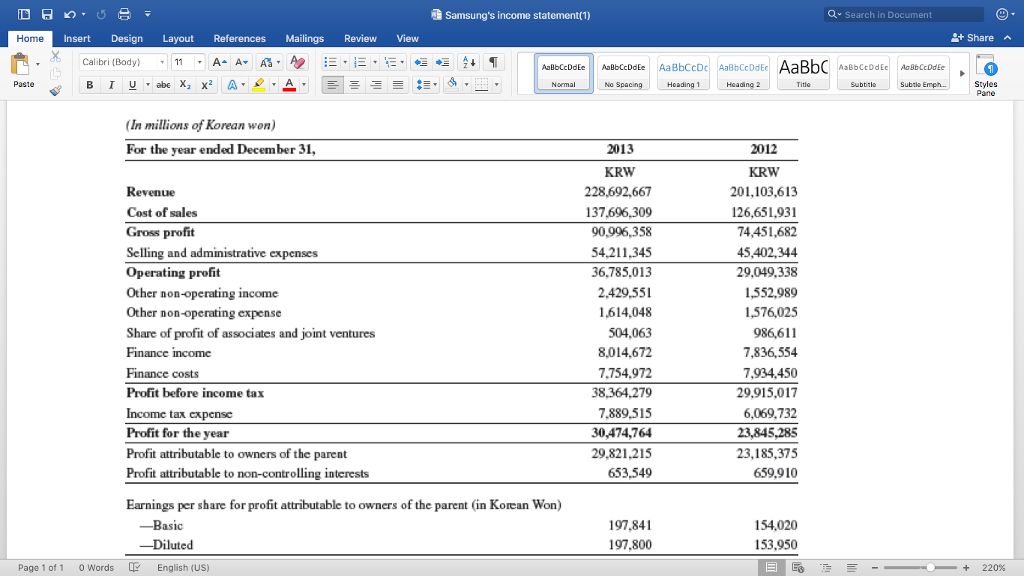
Administrative expenses are costs incurred by an organization that are not directly related to specific core functions such as manufacturing, production, or sales. These overhead expenses are related to the organization as a whole, rather than individual departments or business units.
Key Takeaways:
– Administrative expenses are costs incurred to support the functioning of a business, but are not directly related to the production of a specific product or service.
– Some level of administrative expenses is always necessary for operations.
– Administrative expenses are often the first identified for budget cuts because they do not directly impact a company’s main business functions.
– Management may allocate administrative expenses to business units based on revenue, expenses, or other measures.
Understanding Administrative Expenses:
Administrative expenses may include salaries of senior management and costs associated with general services or supplies, such as legal, accounting, clerical work, and information technology. These costs are not directly related to the production of goods or services and are usually excluded from gross margins.
Companies incur administrative expenses to perform basic operations, increase oversight and efficiency, and comply with laws and regulations. On the income statement, administrative expenses appear below cost of goods sold (COGS) and may be shown with other expenses such as general or selling expenses.
Some administrative expenses are fixed, occurring regardless of production or sales. Others are semi-variable, such as minimum electricity usage. Businesses can reduce these expenses beyond the minimum level.
Since administrative expenses do not directly impact the products sold, they are often the first to be cut from the budget. Maintaining low administrative expenses relative to other costs allows businesses to utilize leverage more effectively. The sales-to-administrative expense ratio helps measure how much sales revenue is used to cover administrative costs.
Companies can deduct reasonable, ordinary, and necessary administrative expenses from their tax returns. These expenses must be incurred during the usual course of business and deducted in the year they occur.
Other Types of Administrative Expenses:
Wages and benefits for certain employees, like accounting and IT staff, are considered administrative expenses. All executive compensation and benefits fall into this category. Building leases, insurance, subscriptions, utilities, and office supplies may also be classified as general or administrative expenses.
Depending on the asset being depreciated, depreciation expenses may be classified as general, administrative, or selling (marketing) expenses. Consulting and legal fees can be considered administrative expenses, but research and development (R&D) costs are not.
To understand the costs of running business units, companies may allocate administrative expenses to each department based on factors like revenue, expenses, or square footage. This allows management to make decisions about expanding or reducing individual business units.
Example of Administrative Expenses:
For example, if XYZ Company spends $4,000 monthly on electricity, it may allocate the cost based on the square footage each department occupies. Assuming:
– Production facility: 2,000 sq ft
– Manufacturing facility: 1,500 sq ft
– Accounting office: 750 sq ft
– Sales office: 750 sq ft
The company occupies a total of 5,000 sq ft. The electric bill could be allocated as follows:
– Production: $1,600 (2,000 / 5,000) x $4,000
– Manufacturing: $1,200 (1,500 / 5,000) x $4,000
– Accounting: $600 (750 / 5,000) x $4,000
– Sales: $600 (750 / 5,000) x $4,000



